Table of Contents
How do you treat antral pseudocyst?
The reason we use this two-step approach for a larger growth is to minimize the risk of complications. We want to ensure the sinus has enough time to heal before we start the reconstruction process. The second step of maxillary sinus floor augmentation involves placing bone grafts or other materials into the sinus cavity to rebuild the floor. This will help to restore the shape and function of the sinus. This process helps to support teeth that may have been affected by the pseudocyst. You’ll work with your doctor to determine the best treatment plan for your specific case.
How do you treat a maxillary antrum cyst?
The cyst may be removed through a minor endoscopic sinus surgery. This surgery is usually very well tolerated, and most people experience minimal discomfort afterwards.
There are two common approaches to removing the cyst:
Enucleation: This involves removing the entire cyst without breaking it open. Think of it like carefully peeling an orange.
Curettage: This method uses a special looped instrument to scrape away the cyst lining. It’s like gently brushing away a bit of paint.
Both approaches are effective in treating maxillary antrum cysts.
What happens during an endoscopic sinus surgery?
The surgery is done under general anesthesia, which means you’ll be asleep. A small telescope-like instrument, called an endoscope, is inserted into your nose. This allows the surgeon to see inside your sinuses and pinpoint the cyst. The cyst is then removed using one of the techniques we just discussed. The entire procedure usually takes about an hour or less.
Why is endoscopic sinus surgery the preferred method?
It’s minimally invasive, which means it involves small incisions and less disruption to your tissues. This leads to a faster recovery time and less scarring. It also offers a clear view of the surgical area, which allows the surgeon to remove the entire cyst while preserving healthy tissue.
What to expect after surgery?
After the procedure, you’ll likely experience some discomfort or swelling, but this is usually managed with over-the-counter pain medication. You may also have a temporary stuffy nose or drainage. The majority of people are able to return to their normal activities within a few days.
It’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully after surgery. This includes taking your medications as prescribed, keeping the surgical area clean, and avoiding strenuous activity.
Recovery:
Full recovery from an endoscopic sinus surgery usually takes a few weeks. You may need to follow up with your doctor for regular checkups to ensure the cyst has been completely removed and that you’re healing well.
Remember, if you have any questions or concerns about treating a maxillary antrum cyst, it’s essential to talk to your doctor. They can provide personalized guidance and answer any questions you may have.
What is a pseudocyst of the maxillary antrum?
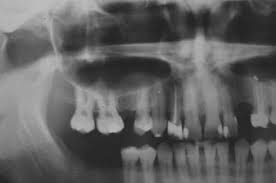
This fluid buildup happens beneath the periosteum, which is the thin membrane that covers the bone of the sinus. The pressure from the fluid pushes the lining of the sinus away from the floor, creating a dome-shaped structure that’s often visible on dental x-rays. In most cases, these pseudocysts are harmless and don’t cause any symptoms.
The exact cause of maxillary retention cysts isn’t fully understood. Some experts believe that they form due to a blockage in the sinus drainage system, which prevents the normal flow of mucus. Others believe they can be caused by trauma to the area, inflammation, or even infection.
It’s important to note that the maxillary antrum, also known as the maxillary sinus, is a hollow space within the maxillary bone, which is one of the bones in your face. It’s connected to the nasal cavity through a small opening called the ostium, which allows mucus to drain from the sinus.
Because most pseudocysts are asymptomatic, they’re often discovered accidentally when a patient is having a dental x-ray done for another reason. If you do experience symptoms such as pain, pressure, or swelling in your face, it’s essential to see a doctor to rule out any other potential problems.
In most cases, maxillary retention cysts don’t require treatment. However, if they cause symptoms or are large enough to interfere with normal sinus function, your doctor may recommend a surgical procedure to remove the pseudocyst.
Do maxillary sinus cysts need to be removed?
It’s true that small lesions may go away on their own. However, if the cyst is causing problems, it will need to be treated. Surgical removal is often the best way to deal with a symptomatic cyst. Curettage or maxillary sinusectomy are common procedures used to remove the cyst.
Here’s why removing a maxillary sinus cyst might be necessary:
Pain: Cysts can cause pain, pressure, and discomfort in the face and sinuses.
Infection: A cyst can become infected, leading to more serious complications like sinusitis.
Blockage: The cyst can block the sinus opening, preventing proper drainage. This can lead to headaches and other symptoms.
Growth: Some cysts can grow quite large, potentially affecting the structure of the sinuses and even pushing on surrounding tissues.
If you have a maxillary sinus cyst, it’s important to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment recommendations. They can determine if the cyst needs to be removed and help you understand your options.
What is the treatment for a pseudocyst?
Another option for draining a pseudocyst is endoscopic drainage. This technique involves using an endoscope, a thin, flexible tube with a camera attached, to reach the cyst. The endoscope is inserted through the mouth or the anus, depending on the location of the cyst. Once the cyst is located, the doctor can then insert a small drainage tube into the cyst.
Both catheter drainage and endoscopic drainage are minimally invasive procedures that can effectively drain the pseudocyst. The choice of procedure depends on the size and location of the cyst, as well as the overall health of the patient.
It’s important to remember that these procedures are not a cure for a pseudocyst, but rather a way to manage the symptoms. The underlying cause of the pseudocyst will need to be addressed to prevent recurrence. This may involve medication, lifestyle changes, or even surgery.
Can a pseudocyst be removed?
Endoscopic drainage is a procedure where a doctor inserts a thin, flexible tube with a camera on the end (endoscope) into the digestive tract. The endoscope allows the doctor to see the pseudocyst and insert a small drain into it. The drain removes fluid from the pseudocyst, which helps it shrink and eventually go away.
Sometimes, though, endoscopic drainage might not be the best choice. If the pseudocyst is very large, in a difficult-to-reach area, or if it’s causing problems like bleeding, surgery might be necessary.
Surgery involves making a small incision in the abdomen and removing the pseudocyst. It’s a more invasive procedure than endoscopic drainage, but it can be the best option in certain cases.
No matter which method is chosen, it’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully and keep all follow-up appointments. This helps ensure the pseudocyst is completely removed and that you recover fully.
What is the most common cyst in the maxillary sinus?
Let’s break down what this means:
Maxillary Sinus: This is an air-filled cavity in the upper jawbone (maxilla). It’s located behind your cheekbones and above your teeth.
Cyst: A cyst is a fluid-filled sac that can form in different parts of the body. In the case of a radicular cyst, it arises from the tip of a tooth root.
Odontogenic: This term means that the cyst is related to the teeth.
A radicular cyst develops when the pulp, the soft tissue inside the tooth, becomes infected. This infection can spread to the tip of the tooth root, causing inflammation. Over time, this inflammation can form a cyst.
Here’s what typically happens:
1. Tooth Decay: A cavity or deep decay can reach the pulp of the tooth.
2. Pulp Infection: The pulp becomes infected.
3. Inflammation: The infection spreads to the area around the tip of the root, causing inflammation.
4. Cyst Formation: A cyst forms as the body tries to wall off the infection.
These cysts are usually slow-growing and can sometimes go unnoticed for years. However, they can cause problems if they become large enough. A radicular cyst can:
Cause Pain: If the cyst presses on surrounding nerves, it can cause toothache or other pain.
Affect Bone: A large cyst can weaken the bone surrounding the tooth, leading to a fracture.
Lead to Infection: If the cyst becomes infected, it can spread to other areas of the face.
If you experience any pain in your teeth or jaw, it’s important to see a dentist for a checkup. They can help determine if you have a radicular cyst and recommend treatment options.
Who treats maxillary cyst?
While surgery is often the go-to treatment for maxillary cysts, there are other options too. In some cases, medical therapy might be used, or a combination of surgery and medical therapy could be the best approach.
It’s important to understand that maxillary cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can form in the upper jawbone. They can vary in size and can sometimes cause pain, swelling, or even tooth loss. The good news is that these cysts are often benign, meaning they’re not cancerous.
To diagnose a maxillary cyst, your oral and maxillofacial surgeon will likely conduct a thorough examination and may order imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, they’ll discuss the best treatment plan with you.
Remember, there’s no need to worry if you’re dealing with a maxillary cyst. With the right treatment from an experienced oral and maxillofacial surgeon, you can get back to a healthy and comfortable life.
What is the difference between pseudocyst and cyst?
A cyst is a closed sac-like structure that’s lined with epithelial cells. It can contain fluid, semi-solid material, or even gas. Think of it like a little balloon with a very specific inner lining.
A pseudocyst, on the other hand, is not a true cyst. It doesn’t have that epithelial lining. Instead, it’s surrounded by a wall of fibrous and granulation tissue. This tissue is essentially scar tissue that forms when the body tries to heal an injury. So, it’s more like a temporary pocket of fluid that’s being held together by the body’s own healing processes.
To put it simply:
Cyst: A true, well-defined sac with a lining.
Pseudocyst: A fluid-filled space without a true lining, just a temporary wall of scar tissue.
Understanding the difference between cysts and pseudocysts is important because it helps doctors determine the best course of treatment. For example, a cyst might be treated with surgery, while a pseudocyst might resolve on its own or with conservative measures.
How serious is a pseudocyst?
A pseudocyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms near the pancreas. It’s not a true cyst because it doesn’t have a lining. Pseudocysts usually develop after an injury to the pancreas, such as pancreatitis. They can also form after surgery or trauma.
Most pseudocysts are small and cause no symptoms. However, some can grow large and cause pain, nausea, vomiting, and even internal bleeding. The most serious complication of a pseudocyst is rupture. This can happen if the pseudocyst becomes very large or if it’s infected. If a pseudocyst ruptures, it can spill its contents into the abdominal cavity, causing a serious infection.
A ruptured pseudocyst is a medical emergency. You should seek immediate medical attention if you have any of the following symptoms:
High, persistent fever
Severe abdominal pain
Rapid heart rate
Low blood pressure
Shock
If you have a pseudocyst, your doctor will monitor it closely. They may recommend treatment, such as surgery or drainage, if the pseudocyst is large, causing symptoms, or at risk of rupture.
See more here: How Do You Treat A Maxillary Antrum Cyst? | Maxillary Sinus Antral Pseudocyst Treatment
See more new information: musicbykatie.com
Maxillary Sinus Antral Pseudocyst Treatment: What You Need To Know
Okay, so you’ve been told you have a maxillary sinus antral pseudocyst, and you’re probably wondering what that even means, let alone how to treat it. Don’t worry, I’m here to break it down for you in a way that’s easy to understand.
What Exactly is a Maxillary Sinus Antral Pseudocyst?
Think of it like a little pocket of fluid or air that forms inside your maxillary sinus, which is the space right above your teeth. These pseudocysts aren’t cancerous or anything, they’re just kinda annoying.
Now, you might be asking, “Why did this happen to me?” Good question! There isn’t always a clear answer. It could be due to a few things:
Sinus infection: Those pesky sinusitis episodes can sometimes lead to pseudocysts.
Trauma: Any kind of head injury or even just a bad sinus surgery could cause one.
Dental work: Yeah, even something like a root canal can make these things pop up.
The cool thing is, most of the time, these pseudocysts are totally harmless. You might not even notice them. But for some people, they can cause some annoying symptoms:
Facial pain: It can feel like a dull ache or pressure around your cheekbones.
Headache: Yep, a headache can be a symptom.
Sinus pressure: That feeling like your sinuses are clogged? That’s another one.
Nasal congestion: If you’re having trouble breathing through your nose, it could be a sign.
So How Do You Deal With These Pseudocysts?
The good news is that most of the time, you don’t have to do anything. They usually go away on their own, or you can just manage the symptoms. Think of it like a little sniffle – you might need a tissue or some decongestant, but you’ll probably get over it in a few days.
But if those symptoms are really bothering you, or the pseudocyst just isn’t going away, there are a few things you can try:
Medications: Your doctor might prescribe antibiotics or nasal corticosteroids to help with infection or inflammation.
Sinus rinses: These can help clear out mucus and make you feel better. You can get saline solutions at the pharmacy or make your own with salt and water.
Surgery: In some cases, your doctor might recommend surgery to remove the pseudocyst. But this is usually only if other treatments haven’t worked, and if the pseudocyst is causing a lot of problems.
Here’s the deal: It’s important to see a doctor if you think you might have a maxillary sinus antral pseudocyst. They can help determine if it’s causing you any issues and suggest the best treatment for your situation.
How to Find the Right Treatment for You
Alright, so you’ve been diagnosed with a maxillary sinus antral pseudocyst, and you’re probably wondering what comes next. Let’s talk about finding the treatment that’s right for you.
It’s all about the symptoms:
No symptoms: If you’re not feeling any of those annoying side effects like pain, pressure, or congestion, then chances are, your doctor will just keep an eye on it.
Mild symptoms: If you’re experiencing some mild symptoms, your doctor might prescribe medications like antibiotics or nasal corticosteroids to help clear up the infection or inflammation.
Severe symptoms: If your symptoms are causing a lot of discomfort or interfering with your daily life, your doctor might recommend a more aggressive approach. This could include sinus surgery to remove the pseudocyst.
Who is the best person to see?
For diagnosis and treatment, you’ll want to see an ENT doctor, also known as an otolaryngologist. These specialists are experts in all things related to the ears, nose, and throat.
Let’s talk about some specifics:
Diagnosis: Your doctor will start with a physical exam and ask you about your symptoms. They may also use imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans to get a better look at your sinuses.
Treatment: The treatment will depend on your symptoms and the size and location of the pseudocyst.
Recovery: Recovery time will vary depending on the type of treatment you receive.
I hope this information helps clear up any confusion you might have about maxillary sinus antral pseudocysts. Remember, if you have any concerns, don’t hesitate to ask your doctor for guidance.
FAQs about Maxillary Sinus Antral Pseudocysts
1. Are maxillary sinus antral pseudocysts contagious?
Nope, they’re not contagious. You can’t catch them from someone else.
2. Can maxillary sinus antral pseudocysts cause cancer?
No, they are not cancerous and do not increase your risk of developing cancer.
3. Can I prevent maxillary sinus antral pseudocysts?
While you can’t completely prevent them, you can reduce your risk by:
Keeping your sinuses healthy: Practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently and avoiding close contact with people who are sick.
Treating sinus infections promptly: If you have a sinus infection, get treatment from your doctor right away.
Avoiding irritants: Stay away from things that can irritate your sinuses, such as smoke, dust, and strong odors.
4. What if I’m worried about the cost of treatment?
That’s understandable. I suggest talking to your doctor about the cost of treatment and exploring options like:
Negotiating payment plans: Some doctors are willing to work with patients to set up payment plans.
Financial assistance programs: There may be financial assistance programs available through your insurance provider or local health organizations.
5. What is the long-term outlook for people with maxillary sinus antral pseudocysts?
The long-term outlook is generally good. Most people with maxillary sinus antral pseudocysts don’t experience any serious complications. And remember, they often go away on their own.
6. I still have questions! Who can I ask?
Your doctor is the best resource for answering any questions you might have about maxillary sinus antral pseudocysts. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific situation.
A Reliable Surgical Procedure for Sinus Floor Augmentation with
An antral pseudocyst (AP) is a common well-defined ‘dome-shaped’ faintly radiopaque lesion of the maxillary sinus, and usually does not require treatment in asymptomatic patients. National Center for Biotechnology Information
A Clinical Approach for the Removal of a Large Antral
For a large benign lesion within the maxillary sinus, such as an antral pseudocyst, maxillary sinus floor augmentation is more commonly performed using a two-stage approach. This National Center for Biotechnology Information
Comprehensive review and proposed treatment algorithm
Antral Pseudocysts (AP) are fairly common lesions of the maxillary sinus and may often be encountered during Maxillary Sinus Augmentation (MSA). The objective of ScienceDirect
Are mucous retention cysts and pseudocysts in the maxillary
Mucous retention cysts and pseudocysts of the maxillary sinus are benign lesions present in up to 13% of adult patients. Different surgical approaches for sinus lift National Center for Biotechnology Information
Maxillary sinus augmentation in the presence of antral
The maxillary sinus augmentation procedure has been routinely performed with predictable results, and is an acceptable, safe modality for bone augmentation, providing a base for endosseous oooojournal.net
A Reliable Surgical Procedure for Sinus Floor Augmentation with
An antral pseudocyst (AP) is a common well-defined ‘dome-shaped’ faintly radiopaque lesion of the maxillary sinus, and usually does not require treatment in PubMed
Maxillary sinus augmentation in the presence of antral
A pseudocyst of the maxillary sinus is not a contraindication for sinus augmentation. The low frequency of sinus membrane perforation and postsurgery ScienceDirect
Maxillary sinus floor augmentation comparing removing versus
Objectives. To retrospectively compare multilevel volumetric changes in both hard and soft tissues between antral pseudocyst (AP) removal and retainment before maxillary Wiley Online Library
Comprehensive review and proposed treatment algorithm
Antral Pseudocysts (AP) are fairly common benign lesions of the maxillary sinus. As its name suggests, an AP is not histologically a true cyst as it is not ScienceDirect
Maxillary sinus floor augmentation: a review of current … – Nature
Maxillary sinus floor augmentation using lateral window and crestal technique is considered as predictable methods to increase the residual bone height; however, this Nature
Maxillary Sinus Retention Cyst Treatment \U0026 Simultaneous Sinus Lift
Antral Pseudocyst / Benign Mucosal Cyst Of Maxillary Antrum
Large Maxillary Sinus Cyst Enucleated By Intra Oral Approach
Maxillary Sinus Diseases | Sinusitis | Oro-Antral Communication/Fistula | Caldwell-Luc Procedure
Maxillary Sinus Cyst Removal
Maxillary Sinus Cyst Enucleation With Antral Lavage
Mucous Retention Pseudocyst And What???
Maxillary Sinus
Link to this article: maxillary sinus antral pseudocyst treatment.
See more articles in the same category here: https://musicbykatie.com/wiki-how/
