Table of Contents
Why Gabriel synthesis is used?
Let’s break this down further. Primary amines are organic compounds containing an amino group (-NH2) directly attached to a carbon atom. They are incredibly versatile and play crucial roles in various chemical reactions and biological processes.
Why is the Gabriel synthesis so valuable? Well, it offers several advantages over other methods for preparing primary amines:
1. High selectivity: The Gabriel synthesis provides a highly selective method to produce primary amines, even in the presence of other functional groups. This is a significant advantage because many other methods tend to produce mixtures of different amines.
2. Mild reaction conditions: The Gabriel synthesis typically proceeds under relatively mild conditions, minimizing the risk of side reactions and making it suitable for a wider range of substrates.
3. High yields: The synthesis often results in high yields of the desired primary amine, making it an efficient and economical method.
4. Flexibility: The Gabriel synthesis is versatile enough to be adapted for synthesizing various types of primary amines, including those with different substituents on the alkyl chain.
Essentially, the Gabriel synthesis is a reliable and efficient way to prepare primary amines with high purity, making it a valuable tool for chemists in academic and industrial settings. It has found wide application in organic synthesis, medicinal chemistry, and the development of various pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
What is the solvent for Gabriel synthesis?
The choice of solvent depends on the specific reaction conditions and the desired outcome. DMF is often preferred because it is a good solvent for both the reactants and the products, and it can dissolve a wide range of organic compounds. It is also relatively inexpensive and readily available.
DMSO is another common solvent used in Gabriel synthesis. It is a polar aprotic solvent with a high dielectric constant, which makes it a good solvent for ionic reactions. DMSO is also a good solvent for many organic compounds, and it can dissolve a wide range of compounds, including those that are not soluble in DMF.
HMPA is a very strong polar aprotic solvent that is often used in reactions involving strong bases. It is a good solvent for many organic compounds, and it can dissolve a wide range of compounds, including those that are not soluble in DMF or DMSO. However, HMPA is toxic and carcinogenic, so its use is generally avoided when other solvents are available.
Acetonitrile is a polar aprotic solvent that is often used in reactions involving nucleophiles. It is a good solvent for many organic compounds, and it can dissolve a wide range of compounds, including those that are not soluble in DMF or DMSO. Acetonitrile is also relatively inexpensive and readily available.
Ethylene glycol is a polar protic solvent that is often used in reactions involving alcohols. It is a good solvent for many organic compounds, and it can dissolve a wide range of compounds, including those that are not soluble in DMF, DMSO, or acetonitrile. However, ethylene glycol is a viscous liquid, which can make it difficult to work with.
The choice of solvent in Gabriel synthesis is an important consideration, as it can affect the reaction rate, yield, and selectivity.
While the original Gabriel synthesis had some limitations, modern research has led to significant advancements, making this method more versatile and applicable to a wider range of substrates.
Why can’t aromatic amines be prepared by Gabriel?
The C-X bond in haloarenes, which are like alkyl halides but with the halogen attached to a benzene ring, is very strong. This is because the bond has some double bond character, making it difficult to break. This is a key reason why Gabriel synthesis doesn’t work for aromatic amines.
Here’s why that double bond character is so important. The lone pair of electrons on the halogen atom in haloarenes can interact with the pi-electron system of the benzene ring. This interaction creates a partial double bond character in the C-X bond, making it much stronger and less reactive. This makes it difficult for the phthalimide anion, which is a strong nucleophile, to attack the carbon atom bonded to the halogen.
Think of it like this: the benzene ring and the halogen are holding hands really tightly, making it hard for the phthalimide anion to break them apart.
To put it simply, aromatic halides just don’t like to undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions with the phthalimide anion. That’s why we can’t make aromatic amines using the Gabriel phthalimide synthesis.
But don’t worry! There are other ways to make aromatic amines, like the Sandmeyer reaction, which uses a different approach to make it happen.
How to reduce nitriles?
Here’s the lowdown:
Nitriles contain a carbon-nitrogen triple bond which makes them quite reactive.
* You can tame these bonds by adding hydrogen gas in the presence of a metal catalyst. This process is called catalytic hydrogenation.
Think of it as the catalyst helping the hydrogen gas to attach to the nitrile molecule, causing a change in the chemical structure.
Common Catalysts
The metal catalysts are the key players in this reaction. Palladium, platinum, and nickel are some popular choices because they are good at facilitating the reaction and making it happen quickly and efficiently. They act like matchmakers for the hydrogen and nitrile molecules.
Understanding Catalytic Hydrogenation
Let’s dive a bit deeper into the catalytic hydrogenation process:
Step 1: Adsorption. The nitrile molecule and hydrogen gas attach themselves to the surface of the catalyst. Think of it like sticking to a sticky surface.
Step 2: Activation. The catalyst weakens the bonds within the nitrile molecule and hydrogen, making it easier for them to break and recombine.
Step 3: Reaction. The hydrogen atoms attach to the carbon and nitrogen atoms of the nitrile, forming a new molecule called an amine.
Step 4: Desorption. The newly formed amine molecule detaches itself from the catalyst’s surface, leaving the catalyst free to continue the process.
It’s like a mini factory where the catalyst is the machine, hydrogen and nitrile are the raw materials, and the amine is the finished product!
Important Considerations
While catalytic hydrogenation is a useful tool for reducing nitriles, there are a few things to keep in mind:
Reaction Conditions: The specific conditions, such as temperature and pressure, can influence the efficiency of the reaction.
Catalyst Choice: The choice of catalyst can influence the rate and selectivity of the reaction. Some catalysts work better than others for specific nitriles.
Safety: Hydrogen gas is flammable, so you need to take safety precautions when working with it.
By understanding these key concepts, you’ll be well on your way to tackling nitrile reduction with confidence!
See more here: What Is Robinson Gabriel Synthesis Used For? | Gabriel Synthesis Is Used For The Preparation Of
Why is Gabriel synthesis limited to the formation of primary amines?
Think of it like trying to build a house with a faulty foundation. The Gabriel synthesis needs a stable foundation, which is provided by a primary alkyl halide. Secondary and tertiary halides are like shaky foundations, leading to unwanted side reactions and a messy outcome.
Another limitation is that aryl halides are not compatible with the Gabriel synthesis. This is because aryl halides are much less reactive than alkyl halides in nucleophilic substitution reactions. The conditions needed for the Gabriel synthesis are too harsh for aryl halides and would lead to undesired reactions instead of the desired amine formation.
Let’s delve a bit deeper into the reason behind these limitations.
The Gabriel synthesis relies on the nucleophilic attack of phthalimide anion on an alkyl halide. This reaction, called SN2 reaction, is favored for primary alkyl halides because they are less hindered and allow the nucleophile to approach the carbon atom easily. Secondary and tertiary alkyl halides are more sterically hindered due to the presence of more alkyl groups around the carbon atom. This makes it difficult for the phthalimide anion to approach and react. Instead, a competing reaction, elimination reaction, takes over.
In an elimination reaction, a base removes a proton from a carbon atom adjacent to the carbon atom with the halide. This leads to the formation of a double bond and the removal of the halide. Since secondary and tertiary alkyl halides are more prone to elimination reactions, they are not suitable substrates for the Gabriel synthesis.
Aryl halides are even less reactive than secondary and tertiary alkyl halides because of the resonance effect of the aromatic ring. The electron density is delocalized over the entire ring, making the carbon atom attached to the halogen less electrophilic. This makes the nucleophilic attack on aryl halides very difficult, and the Gabriel synthesis fails to yield the desired product.
In essence, the Gabriel synthesis is a powerful tool for primary amine synthesis but has limitations due to the inherent reactivity of different types of halides. Understanding these limitations helps us choose the appropriate method for our specific synthetic goals.
See more new information: musicbykatie.com
Gabriel Synthesis Is Used For The Preparation Of | Which Of The Following Can Be Prepared By Gabriel Synthesis?
Gabriel Synthesis – Chemistry LibreTexts
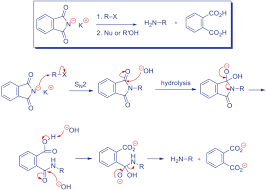
The goal of Gabriel synthesis is to create a primary amine (RNH 2). Doing a direct S N 2 reaction would result in a quaternary amine salt, which can be pretty useless (unless you use Hofmann elimination). Before we get into the mechanism, let’s look at Chemistry LibreTexts
The Gabriel Synthesis – Master Organic Chemistry
The Gabriel synthesis of amines is the reaction of a phthalimide salt with an alkyl halide followed by hydrolysis. Examples, mechanism, and more below. Skip to content Master Organic Chemistry
Gabriel Phthalimide Synthesis Mechanism
What is Gabriel Phthalimide Synthesis Reaction? Gabriel Phthalimide Synthesis Mechanism has 3 steps. The Synthesis is used to get primary amines from primary alkyl halides and is named after the German BYJU’S
Gabriel Synthesis – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Gabriel synthesis is a classical method used to prepare primary amines by alkylating phthalimide anion with an appropriate alkylating reagent and subsequently removing the ScienceDirect
Gabriel Synthesis – Chemistry LibreTexts
The Gabriel synthesis is a three-stage procedure used to prepare primary aliphatic amines from the corresponding organic halides. Chemistry LibreTexts
The Gabriel Synthesis: A Method for Producing Primary Amines
The Gabriel Synthesis is an essential organic chemistry technique developed by Siegmund Gabriel for synthesizing primary amines from alkyl halides. It utilizes algoreducation.com
The Gabriel Synthesis – Chemistry Steps
Let’s put together a summary of the Gabriel reaction for preparing1° amines in which the overall result is nucleophilic substitution of X by NH 2, so the Gabriel synthesis can be used: Now, the amide hydrolysis is often Chemistry Steps
Gabriel Synthesis – Organic Chemistry Portal
Gabriel Synthesis. Potassium phthalimide is a -NH 2-synthon which allows the preparation of primary amines by reaction with alkyl halides. After alkylation, the phthalimid is not nucleophile and does not react anymore. Organic Chemistry Portal
Gabriel Synthesis – Springer
Siegmund Gabriel (1851 1924), born in Berlin, Germany, studied under Hofmann at Berlin and Bunsen in Heidelberg. He taught at Berlin, where he discovered the Gabriel Springer
Gabriel Synthesis Reaction Mechanism – Alkyl Halide To Primary Amine
Gabriel Amine Synthesis
Gabriel Synthesis Is Used For The Preparation Of
Gabriel Phthalimide Synthesis Is Used For The Preparation Of (A) Primary Aromatic Amines (B) Pri…
Gabriel’S Phthalimide Synthesis Is Used For The Preparation Of (A) Primary Aromatic Amines (B) Se…
Link to this article: gabriel synthesis is used for the preparation of.
See more articles in the same category here: musicbykatie.com/wiki-how
