Table of Contents
Which is dominant in pea plant violet or white?
Now, let’s dive a little deeper. The reason purple is dominant is because of something called genes. Each plant inherits two copies of every gene, one from each parent. The gene for flower color can be either purple or white.
* If a plant has two purple genes, it will have purple flowers.
* If a plant has one purple gene and one white gene, it will still have purple flowers, because purple is dominant.
* It’s only when a plant has two white genes that it will have white flowers.
This is how purple becomes the dominant color. You can think of it like a superpower – the purple gene is stronger and wins out! You can learn a lot about genetics by studying pea plants, which is why they’re so popular for scientific experiments.
What is the dominant flower position in pea plant?
But how do axial flowers differ from the other kind? Terminal flowers are located at the very tip of the stem, kind of like the final boss of a plant. On the other hand, axial flowers are found along the stem, like little side quests you get to explore. This is all because of the gene that controls the position of these flowers.
Think of it like this: Imagine you have a pea plant with the axial gene. It’s like having a superpower that makes the plant produce axial flowers. Even if the plant also inherits the gene for terminal flowers from the other parent, the axial gene will always win, and the plant will still show axial flowers.
Here’s a simple breakdown:
Axial (A) – Dominant. The plant will have axial flowers.
Terminal (a) – Recessive. The plant will only have terminal flowers if it inherits both terminal genes from both parents.
So, there you have it! Axial flower position in pea plants is the dominant trait, meaning it’s more likely to appear in offspring than its recessive counterpart, terminal flower position.
What does “purple flowers are dominant to white flowers” mean?
Think of it like a game of tug-of-war. The purple gene is stronger, pulling the flower color towards purple even if there’s a white gene trying to pull it towards white.
The white gene, in this case, is called a recessive trait. It can only express itself if the plant inherits two white genes. If it has one purple gene, the purple trait will always win out.
This is why you might see a plant with purple flowers even though it carries the gene for white flowers. The purple trait masks the white trait. It’s like a superhero with a secret identity! The purple flower is the superhero, and the white flower gene is its hidden identity, only revealed when the plant inherits two white genes.
In a group of 400 plants, we expect to see only 100 with two white genes (homozygous recessive). This is because the chance of inheriting two white genes is lower compared to inheriting at least one purple gene.
Now, you might be wondering how we know these genes are dominant or recessive. That’s where genetics comes in! By studying how traits are passed down through generations, we can figure out which genes are dominant and which are recessive. It’s like a detective story, figuring out the clues to understand the mystery of inheritance.
Are white flowers dominant or recessive in pea plants?
Let’s break down what that means. Imagine each pea plant has two “copies” of the gene for flower color. These copies are called alleles. One allele comes from the “mom” plant, and the other from the “dad” plant. There are two possible alleles for flower color:
Purple flower allele (represented by the uppercase letter P)
White flower allele (represented by the lowercase letter p)
A plant with two P alleles (PP) or one P and one p allele (Pp) will have purple flowers. This is because the purple flower allele is dominant. It “masks” the effect of the white flower allele.
A plant only has white flowers if it has two p alleles (pp). This is because both alleles are recessive. Since there isn’t a dominant purple allele to mask it, the white flower allele is expressed.
So, when we say white flowers are recessive, it means a plant needs two copies of the white flower allele to express the trait. It’s like a hidden superpower that only shows up when there’s no other allele around to overpower it!
Is purple dominant in pea plants?
Purple flowers are dominant over white flowers in pea plants. This means that if a pea plant inherits even one purple flower allele (P), it will express purple flowers.
You’re right to point out that a cross between two pea plants can produce offspring with a 50/50 split of purple and white flowers. This tells us something very important about the parents: they both must carry one purple (P) allele and one white (p) allele. This combination is called heterozygous, meaning they have two different alleles for the flower color trait.
Here’s how the inheritance works:
Parent 1:Pp (one purple allele and one white allele)
Parent 2:Pp (one purple allele and one white allele)
When these parents reproduce, their offspring inherit one allele from each parent. Here are the possible combinations:
PP: Purple flowers (dominant)
Pp: Purple flowers (dominant)
pP: Purple flowers (dominant)
pp: White flowers (recessive)
As you can see, there’s a 3 in 4 chance (75%) of the offspring having purple flowers, and a 1 in 4 chance (25%) of having white flowers.
The 50/50 split you mentioned means that the offspring were likely a result of a specific combination of alleles being passed down. It’s important to remember that inheritance is a matter of probability, and the actual results of a cross can vary.
Which color of pea is dominant?
For the seed color, yellow is dominant over green. This means that if a pea plant has one yellow gene and one green gene, the seeds will be yellow. To get green seeds, the plant needs two green genes.
But it gets a little different when you look at the fruit, or the pod. For pod color, green is dominant over yellow. So, if a plant has one green gene and one yellow gene, the pods will be green. You’ll only get yellow pods if the plant has two yellow genes.
It’s kind of like a genetic game of hide and seek! The dominant gene hides the recessive gene, even if the plant has both.
Here’s a little more about how this works:
Dominant and Recessive Genes:
Dominant genes are like the strong players in the game. They show up even if they’re paired with a weaker gene. They kind of “win” and determine the trait you see.
Recessive genes are like the shy players. They only show up if they’re paired with another recessive gene. It’s like they need a teammate to be seen!
So, to recap:
Yellow seed color is dominant over green seed color.
Green pod color is dominant over yellow pod color.
Think of it like this:
Yellow seeds are like the popular kids who always get their way.
Green pods are like the confident athletes who win every time.
It’s a pretty cool way to think about how genes work!
What are the 4 dominant traits of pea plants?
You’re probably familiar with the classic experiment that helped shape our understanding of genetics: Gregor Mendel’s pea plant studies.
Mendel observed four key traits in pea plants, traits that would go on to become the cornerstone of his groundbreaking work. These are:
Pea shape: Round or wrinkled
Pea color: Green or yellow
Pod shape: Constricted or inflated
Pod color: Green or yellow
So, what makes these traits so important? Well, they were easily distinguishable, meaning Mendel could easily see and categorize the differences. He also chose to focus on two contrasting forms of each trait, which made it easier to track inheritance patterns.
Let’s dive into a bit more detail about each of these traits:
Pea Shape: The difference between round and wrinkled peas lies in the amount of starch present. Round peas have a higher concentration of starch, which makes them appear smooth and full. On the other hand, wrinkled peas contain less starch and have a higher concentration of sugar. This leads to a wrinkled appearance as the peas lose water during maturation.
Pea Color: The color of the pea is determined by the amount of chlorophyll present. Green peas have a higher amount of chlorophyll, which gives them their characteristic green color. Yellow peas have a lower amount of chlorophyll and therefore appear yellow.
Pod Shape: The shape of the pod is defined by its constriction. Constricted pods have a pinched appearance, while inflated pods have a smooth, rounded shape. This difference is also related to the amount of starch present.
Pod Color: Similar to pea color, pod color is determined by the amount of chlorophyll present. Green pods have a higher amount of chlorophyll, while yellow pods have a lower amount.
Mendel’s meticulous observation of these four key traits allowed him to formulate his groundbreaking laws of inheritance, paving the way for our understanding of genetics as we know it today. He proved that traits are inherited in predictable patterns, laying the foundation for future research and the development of modern genetics.
Why yellow is dominant in pea plant?
The yellow version of the pea color gene, symbolized by Y, is dominant over the green version, symbolized by y. This means that if a pea plant inherits even one copy of the Y gene, it will produce yellow peas. The only way for a pea plant to produce green peas is if it inherits two copies of the y gene.
Let’s break it down further: each pea plant has two copies of the pea color gene. When a pea plant produces seeds, it only passes one copy of this gene to each seed. If a pea plant has one Y gene and one y gene, it will produce yellow peas because Y is dominant. If a pea plant has two y genes, it will produce green peas.
Think of it like a coin toss! If you flip a coin, you have a 50/50 chance of getting heads or tails. Similarly, if a pea plant has one Y and one y gene, it has a 50/50 chance of passing on either gene to its offspring. However, because Y is dominant, the offspring will be yellow even if it receives the y gene.
This dominance pattern is a key aspect of Mendelian genetics, named after the pioneering monk Gregor Mendel who studied pea plants in the 19th century. His experiments helped to unveil the fundamental principles of heredity, forming the basis for our understanding of genetics today.
This dominant trait, where the presence of a single Y gene results in yellow peas, explains why yellow peas are so common in nature. It’s a fascinating example of how simple genetic mechanisms can lead to diverse observable traits in living organisms.
See more here: What Is The Dominant Flower Position In Pea Plant? | In Pea Plants Purple Flowers Are Dominant Over White Flowers
Are purple flowers dominant over white flowers in garden peas?
Let’s say we cross two plants that both have purple flowers. We get 324 purple flower plants and 103 white flower plants. Now, let’s think about what this tells us about the genotypes of the parent plants.
We know that the white flower plants must have two white flower genes. This is because the white flower trait is only expressed if the plant has two copies of the white flower gene.
The purple flower plants could have one purple flower gene and one white flower gene, or they could have two purple flower genes. This is because the purple flower trait is dominant, so it will be expressed even if the plant only has one copy of the purple flower gene.
Since we have white flower plants in our offspring, we know that at least one of the parent plants must have been carrying a white flower gene. This is because the white flower trait can only be passed on if one of the parents carries the white flower gene.
So, the genotypes of the parent plants are likely Pp and Pp where P represents the purple flower gene and p represents the white flower gene.
Here’s a deeper dive into the genetics of these purple and white flowers:
Genes and Alleles
Genes: The basic unit of heredity. Genes are responsible for traits like flower color.
Alleles: Different versions of a gene. For example, in garden peas, there’s a gene for flower color, and it has two alleles: one for purple and one for white.
Dominant Allele: An allele that masks the expression of another allele. In our case, the purple flower allele is dominant over the white flower allele.
Recessive Allele: An allele that is masked by a dominant allele. The white flower allele is recessive.
Genotype and Phenotype
Genotype: The genetic makeup of an organism. This refers to the specific combination of alleles an organism carries.
Phenotype: The observable characteristics of an organism, determined by its genotype and environment. For example, the phenotype of a plant is its flower color.
The Punnett Square
The Punnett square is a tool used to predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring from a cross.
* To create a Punnett Square, we list the possible gametes (sperm and egg cells) of each parent along the top and side of the square.
* Each box represents a possible combination of alleles from the parents.
In our case, we have two parent plants with Pp genotypes.
* Parent 1 gametes: P and p
* Parent 2 gametes: P and p
The Punnett square would look like this:
| | P | p |
|———|————–|————–|
| P | PP (Purple) | Pp (Purple) |
| p | Pp (Purple) | pp (White) |
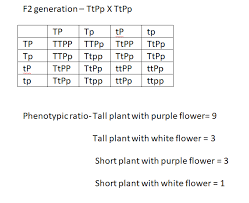
From this, we can see the expected offspring ratios:
PP: 1/4 (25%) – Purple
Pp: 2/4 (50%) – Purple
pp: 1/4 (25%) – White
This aligns with the observed ratio of purple to white flowers, 324:103, which is approximately 3:1. This ratio is consistent with the expected ratio from a cross between two heterozygous plants (Pp x Pp).
So, while we can’t definitively state the exact genotypes of the parents without more information, we can conclude that both plants must have been carrying at least one white flower gene (p) to produce white flower offspring. The most likely genotype for both parent plants is Pp, as this would give us the observed 3:1 ratio of purple to white flowers.
Which flower color is dominant in peas?
Let’s imagine we have a white, short plant and a purple, tall plant. When these two plants are crossed, their offspring will inherit genes from both parents. The white, short plant will have two white flower genes and two short height genes. The purple, tall plant will have at least one purple flower gene and at least one tall height gene.
Because purple flower color is dominant, offspring will have purple flowers if they inherit even one purple flower gene. Similarly, tall height is dominant over short height, so offspring will be tall if they inherit at least one tall height gene.
To figure out the exact percentage of offspring with white flowers and short height, we’d need to know the specific genes of the purple, tall parent. But we can say for sure that some offspring will have white flowers and short height because the white, short parent is contributing those genes.
Here’s why understanding dominant traits is crucial for plant breeders. They can use this knowledge to predict the traits of offspring and select for desired characteristics, such as specific flower colors or plant heights. This process is called selective breeding and has been used for centuries to improve crop yields, enhance food quality, and create new varieties of plants.
For example, imagine a farmer wants to grow peas with purple flowers and tall height. By crossing purple, tall plants with each other, they can increase the chances of producing more plants with these desired traits. By understanding dominant traits, farmers can guide their breeding efforts and improve their harvests.
What color is a purple pea plant?
We know that purple flowers are dominant to white flowers in pea plants. This means that if a plant has at least one P allele, it will have purple flowers. The allele is a version of a gene. If both alleles are p, then the plant will have white flowers.
We also know that yellow peas are dominant to green peas. So, if a plant has at least one Y allele, it will have yellow peas. But if both alleles are y, then the plant will have green peas.
So, what happens when we cross a PpYY plant with a ppYy plant?
Let’s break down the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring:
Genotype: The genetic makeup of an organism.
Phenotype: The observable characteristics of an organism.
PpYY plant has one P allele and one p allele for flower color, and two Y alleles for pea color.
ppYy plant has two p alleles for flower color, one Y allele and one y allele for pea color.
When we cross these two plants, we get the following genotypes and phenotypes for the offspring:
PpYY: Purple flowers, yellow peas
PpYy: Purple flowers, yellow peas
ppYY: White flowers, yellow peas
ppYy: White flowers, yellow peas
The phenotype of the offspring is determined by the genotype. In this case, the offspring will have either purple flowers or white flowers, and all of the offspring will have yellow peas.
Understanding Dominant and Recessive Traits:
Dominant traits are those that are expressed even if only one copy of the allele is present. In this case, purple flowers and yellow peas are dominant traits. Recessive traits are only expressed if both copies of the allele are present. So, a pea plant needs two p alleles to have white flowers and two y alleles to have green peas.
This is an example of Mendelian inheritance, named after Gregor Mendel, the father of genetics. Mendel studied pea plants and discovered the fundamental principles of inheritance.
It’s fascinating how simple combinations of alleles can create such diverse expressions!
Are purple flowers dominant over white flowers?
Purple flowers are indeed dominant over white flowers in pea plants. This means that if a plant inherits even one P allele (gene variant), it will have purple flowers. To have white flowers, a plant must inherit two p alleles.
In our example, two purple-flowered plants are crossed, resulting in 324 purple and 103 white offspring. This ratio tells us a lot about the parents’ genotypes. Let’s break it down:
Purple flowers: We know that purple flowers can be produced by PP or Pp genotypes.
White flowers: White flowers are only produced by the pp genotype.
Since 103 of the offspring are white, both parent plants must have carried a p allele. If one parent was PP, all offspring would be purple.
The fact that a significant number of offspring are white suggests both parents are Pp (heterozygous). This means they each carry one dominant P allele and one recessive p allele. When these plants are crossed, the possible offspring genotypes are PP, Pp, and pp.
Let’s summarize this in a Punnett square:
| | P | p |
|——-|———|———|
| P | PP | Pp |
| p | Pp | pp |
The offspring ratio is approximately 3:1, which is consistent with a cross between two heterozygous parents.
Here’s a deeper dive into why purple flowers are dominant in pea plants:
The color of the flower is determined by a specific gene that codes for an enzyme responsible for producing a purple pigment called anthocyanin. If a plant has at least one copy of the dominant P allele, it produces this enzyme and thus displays purple flowers. Plants with the recessive p allele lack the functional enzyme, resulting in a lack of anthocyanin production and white flowers.
Understanding dominant and recessive traits is crucial for understanding inheritance patterns in plants and animals. It allows us to predict the likelihood of certain traits appearing in offspring and to better understand the genetic makeup of organisms.
See more new information: musicbykatie.com
In Pea Plants, Purple Flowers Are Dominant Over White Flowers: Understanding Mendelian Genetics
Let’s dive into the world of pea plants, where the color of their flowers tells a story about genetics. You might have heard that purple flowers are dominant over white flowers in pea plants. But what does that really mean?
Imagine you’re like a detective trying to crack a code, and the code in this case is about how traits are passed down from parents to offspring. It all boils down to genes, tiny little packages of information that hold the blueprints for an organism’s traits. Think of these genes as the instructions for building a flower.
The Power of Dominant Genes
In our pea plant mystery, there are two key players: alleles. These are different versions of the same gene. One allele is responsible for purple flowers, while the other is responsible for white flowers. Now, here comes the twist: the purple flower allele is dominant!
This means that if a pea plant inherits even just one purple flower allele, it’ll have purple flowers. It’s like the purple flower allele is the boss, shouting over the white flower allele, “My color is the one that’s going to show!”
The Recessive Gene Hides Out
The white flower allele is considered recessive. It can only show up if the plant inherits two copies of the white flower allele, one from each parent. Think of it as the white flower allele being a shy kid who only comes out to play when they’re with their identical twin.
Let’s Do a Quick Breakdown
Here’s how it works:
PP: This represents a pea plant with two purple flower alleles. It will have purple flowers because purple is dominant.
Pp: This pea plant has one purple flower allele and one white flower allele. It will still have purple flowers because the purple flower allele is in charge.
pp: This pea plant has two white flower alleles. Only then does the white flower allele get to shine through, resulting in white flowers.
A Little Experiment: Punnett Squares
To understand these allele combinations even better, we can use a tool called a Punnett square. It’s basically a chart that helps us predict the possible offspring from a cross between two parents.
Imagine we’re crossing two pea plants, one with Pp (purple flowers) and the other with pp (white flowers). Here’s how the Punnett square would look:
| | p | p |
| —- | —— | —— |
| P | Pp | Pp |
| p | pp | pp |
The boxes show the possible combinations of alleles the offspring could inherit:
Pp: Purple flowers
Pp: Purple flowers
pp: White flowers
pp: White flowers
The results show that we’d expect a 50% chance of the offspring having purple flowers and a 50% chance of them having white flowers.
Beyond Pea Plants
The dominant-recessive pattern isn’t just for pea plants. It applies to a lot of traits in different organisms, from humans to animals and even bacteria. Think about eye color or hair color in humans – these are traits that are often influenced by dominant and recessivealleles.
Exploring the World of Genetics
Understanding dominance and recessiveness is just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to genetics. There’s a whole world of fascinating things to learn about how traits are inherited, how they can be influenced by the environment, and how variations arise in populations.
So, the next time you see a pea plant with purple flowers or a white flower, remember that they’re not just pretty faces. They’re a visual representation of the fundamental principles of genetics that govern life on Earth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are some other examples of dominant and recessive traits in pea plants besides flower color?
Aside from flower color, there are a number of other traits in pea plants that display dominant-recessive patterns. Here are a few:
Seed Shape: Round seeds are dominant over wrinkled seeds.
Seed Color: Yellow seeds are dominant over green seeds.
Pod Shape: Inflated pods are dominant over constricted pods.
Pod Color: Green pods are dominant over yellow pods.
Stem Height: Tall plants are dominant over short plants.
If a pea plant has purple flowers, can I be sure it’s PP (two purple flower alleles)?
No, you can’t be absolutely sure. The plant could be either PP or Pp. Both combinations will result in purple flowers because purple is dominant. To figure out the exact allele combination, you would need to perform a test cross, which involves breeding the plant with a white flower plant (pp) and observing the offspring.
What is a test cross?
A test cross is a special kind of breeding experiment used to determine the genotype (the actual alleles a plant has) of an individual with a dominant phenotype (the observable trait). You cross the individual in question with a homozygous recessive individual (e.g., pp for flower color). The offspring’s phenotype will reveal the genotype of the individual with the dominant phenotype.
Can environmental factors affect the color of a pea plant’s flowers?
While alleles are primarily responsible for flower color in pea plants, environmental factors can also play a role. For example, nutrient deficiencies or extreme temperatures might affect the intensity of flower color or even influence the expression of certain alleles. However, these environmental influences generally don’t change the fundamental dominant-recessive relationship between the purple flower allele and the white flower allele.
What is the significance of studying dominant and recessive traits in pea plants?
Studying dominant-recessive inheritance in pea plants helped lay the foundation for our understanding of genetics. Gregor Mendel’s work with pea plants in the 19th century revolutionized our understanding of how traits are passed down from one generation to the next. His experiments established the fundamental principles of genetics that are still relevant today. Understanding these principles is crucial for fields like agriculture, medicine, and even conservation biology.
Punnett square practice Flashcards | Quizlet
In pea plants, purple flowers are dominant to white flowers. If two white flowered plants are crossed, what percentage of their offspring will be white flowered? Quizlet
In the pea plant, purple colour of flower is dominant over white
If pure purple flowered plants are crossed with white flowered plants, all plants of F 1 generation are heterozygous purple flowered plants. Upon self-pollination of F 1 BYJU’S
8.2: Laws of Inheritance – Biology LibreTexts
In pea plants, purple flowers (P) are dominant to white (p), and yellow peas (Y) are dominant to green (y). What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes for a cross between PpYY and ppYy pea Biology LibreTexts
12.3 Laws of Inheritance – Biology for AP® Courses | OpenStax
In pea plants, purple flowers (P) are dominant to white flowers (p) and yellow peas (Y) are dominant to green peas (y). What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes for a OpenStax
Mendel’s Laws – Mendelian Genetics – Wyzant Lessons
Mendel studied several different traits of a pea plant. For example, some pea plants have purple flowers and others have white flowers. Pea plants can either self-fertilize or cross-fertilize. Crossing two plants is called Wyzant
16.2: Mendel’s Experiments and Laws of Inheritance
In the F2 generation, approximately three-quarters of the plants had violet flowers, while one-quarter had white flowers. The offspring of the P generation are called the F1 (for filial, or “offspring”) generation. Biology LibreTexts
In pea plants, purple flowers (P) are dominant over white (p – Quizlet
In pea plants, purple flowers (P) are dominant over white (p) flowers. A cross between two pea plants produces offspring in which approximately 50% of the flowers are white Quizlet
In pea plants, purple flowers are dominant over white flowers.
In pea plants, purple flowers are dominant over white flowers. Two plants, both heterozygous for the gene that controls flower color, are crossed. What percentage of Homework.Study.com
5. In Pea Plants Purple Flowers Are Dominant To White Flowers. A Purple Plant With An Unknown Genot…
A Pea Plant With Purple Flowers Was Crossed With White Flowers Producing All 50 Plants
In Pea Plants, Purple Flowers Are Dominant To White. Complete The Chart Showing The Genotypes And P…
In Pea Plants, Purple (P) Flower Color Is Dominant To White (P) Flowers, And Yellow (Y) Seeds Are D…
Heterozygous Purple Flower Is Crossed With Recessive White Flower. The Progeny Has The Ratio:
The Punnett Square: Purple \U0026 White Flowers – Genetics | Lecturio
A Homozygous Purple Flower Variety Of Pea [Pp] Is Crossed With White Flower Variety Of Pea [P. A…
Mendel’S Experiment | Monohybrid Cross | Law Of Segregation
Link to this article: in pea plants purple flowers are dominant over white flowers.
See more articles in the same category here: https://musicbykatie.com/wiki-how/
