Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Does the resting membrane potential of a neuron change if the extracellular K+ is increased?“? We answer all your questions at the website Musicbykatie.com in category: Digital Marketing Blogs You Need To Bookmark. You will find the answer right below.
A change in extracellular Na+ results in little change to resting membrane potential because the plasma membrane of a neuron is only slightly permeable to Na+ because it contains relatively few Na+ leakage channels. This inhibits net diffusion of Na+ into or out of the cell.Predict what will happen to the resting membrane potential if the extracellular K+ concentration is increased. The resting membrane potential will become more positive (less negative).What generates the resting membrane potential is the K+ that leaks from the inside of the cell to the outside via leak K+ channels and generates a negative charge in the inside of the membrane vs the outside. At rest, the membrane is impermeable to Na+, as all of the Na+ channels are closed.
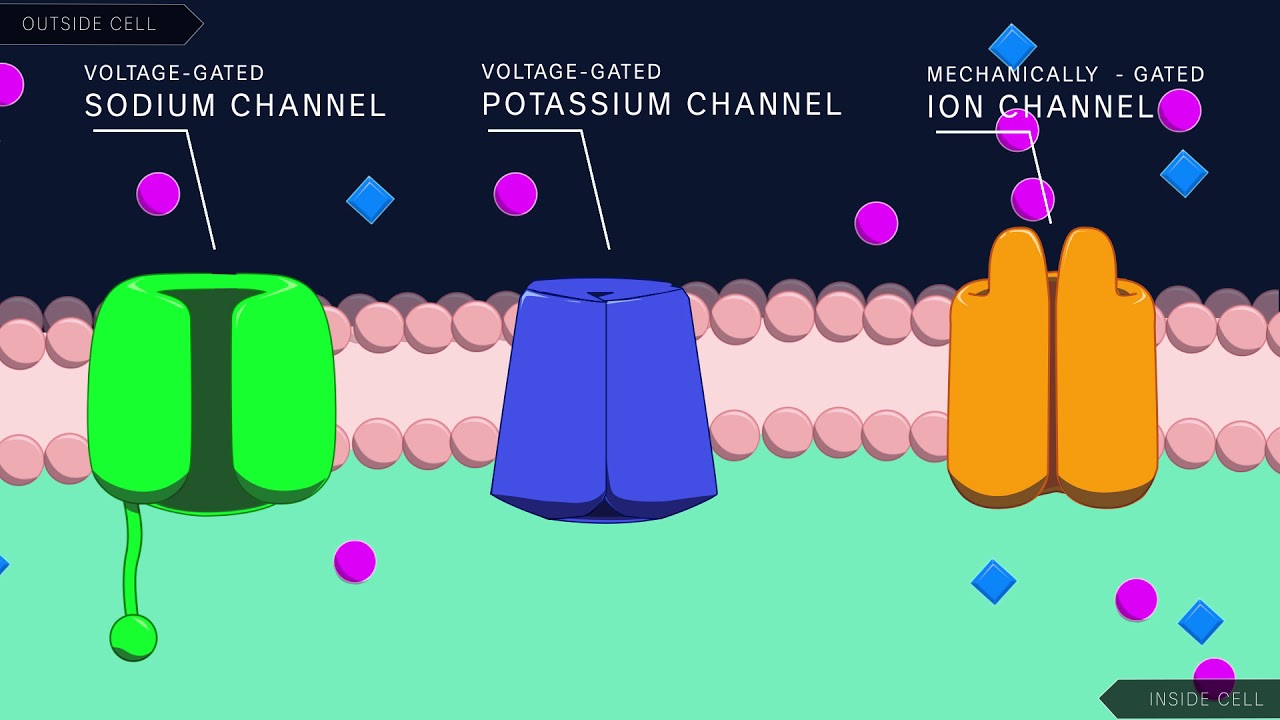
Table of Contents
What happened to the resting membrane potential when the extracellular K+ concentration was increased?
Predict what will happen to the resting membrane potential if the extracellular K+ concentration is increased. The resting membrane potential will become more positive (less negative).
How does K+ affect resting membrane potential?
What generates the resting membrane potential is the K+ that leaks from the inside of the cell to the outside via leak K+ channels and generates a negative charge in the inside of the membrane vs the outside. At rest, the membrane is impermeable to Na+, as all of the Na+ channels are closed.
Action Potential in the Neuron
Images related to the topicAction Potential in the Neuron

How does extracellular potassium affect action potential?
Potassium ions are released during each action potential and accumulate during sustained muscle contraction, rising up to 9 mM during intense exercise [4]. This increase in extracellular potassium ion concentration tends to depolarize the transmembrane resting potential.
What happens if you increase extracellular K +?
Increasing the extracellular potassium reduces the steepness of the concentration gradient and so less potassium diffuses out of the neuron.
What happens if you increase extracellular potassium concentration?
During cardiac disturbances such as ischemia and hyperkalemia, the extracellular potassium ion concentration is elevated. This in turn changes the resting transmembrane potential and affects the excitability of cardiac tissue.
What effect would decreasing the concentration of extracellular potassium ions have on the resting membrane potential of a neuron?
What effect would decreasing the concentration of extracellular potassium ions have on the transmembrane potential of a neuron? More potassium would leave the cell, and the electrical gradient across the membrane (the transmembrane potential) would increase.
What increases resting membrane potential?
Resting Membrane Potential
Increases in activity of the sodium-potassium ATPase pump have been reported with maturation. The increase in sodium-potassium ATPase activity noted during development may in part result from expression of different isoforms of the sodium-potassium ATPase pump.
See some more details on the topic Does the resting membrane potential of a neuron change if the extracellular K+ is increased? here:
Membrane potential (resting membrane potential) (article)
A resting (non-signaling) neuron has a voltage across its membrane called the resting membrane potential, or simply the resting potential.
Resting Potentials and Action Potentials (Section 1, Chapter 1 …
A change in potential that increases the polarized state of a membrane is called a hyperpolarization. The cell is more polarized than it was normally. Use yet a …
Resting Membrane Potential | Biology for Majors II – Lumen …
A neuron at rest is negatively charged: the inside of a cell is approximately 70 millivolts more negative than the outside (−70 mV, note that this number …
Biology – Swarthmore College
Conversely, a change in extracellular potassium potential will lead to a change in the relative volume of the cell and alter the membrane potential.
What effect did decreasing the extracellular sodium have on the resting membrane potential?
The resting membrane potential disappeared. The resting membrane potential became less negative. Only a small change occurred, because the resting neuron is not very permeable to sodium. Only a small change occurred, because the sodium channels were mostly open.
Does the resting membrane potential of a neuron change if the extracellular K+ is increased from 4 mM to 6 mM 1 point?
Does the resting membrane potential of a neuron change if the extracellular K+ is increased from 4 mM to 6 mM? B) YES. The resting membrane potential moves further away from threshold.
Resting membrane potential – definition, examples
Images related to the topicResting membrane potential – definition, examples
How will increasing extracellular potassium affect the Signalling capability of a neuron?
How will increasing extracellular potassium affect the signaling capability of a neuron? Increased extracellular potassium will depolarize the neuron and make it more likely to undergo an action potential. This occurs because the concentration gradient of potassium across the cell membrane is reduced.
How does increasing extracellular potassium depolarize neurons?
Because the resting neuronal membrane is highly permeable to K+, the membrane potential is sensitive to changes in the extracellular potassium concentration – increasing extracellular potassium depolarizes neurons.
How does altering extracellular K+ alter the resting potential?
Resting membrane potential is negative because the negative charge inside the cell is greater than the positive charge outside the cell. Increasing extracellular K+ increases the positive charge outside the cell. This decreases the difference between the inside and outside of the cell.
How does a drop in extracellular potassium affect membrane potential?
In hyperkalemia, the resting membrane potential is decreased, and the membrane becomes partially depolarized. Initially, this increases membrane excitability. However, with prolonged depolarization, the cell membrane will become more refractory and less likely to fully depolarize.
Which would result from an increase in the extracellular concentration of K+ above normal?
13. Which would result from an increase in the extracellular concentration of K+ above normal? C. The potassium equilibrium potential of nerve cells would become more negative.
How would an increase in extracellular K+ affect repolarization?
How would an increase in extracellular K+ affect repolarization? It will decrease the concentration gradient, causing less K+ to flow out of the cell during repolarization. * As extracellular K+ increases, the concentration gradient between the intracellular K+ and extracellular K+ will become less steep.
What causes a resting potential to develop in a neuron?
A resting (non-signaling) neuron has a voltage across its membrane called the resting membrane potential, or simply the resting potential. The resting potential is determined by concentration gradients of ions across the membrane and by membrane permeability to each type of ion.
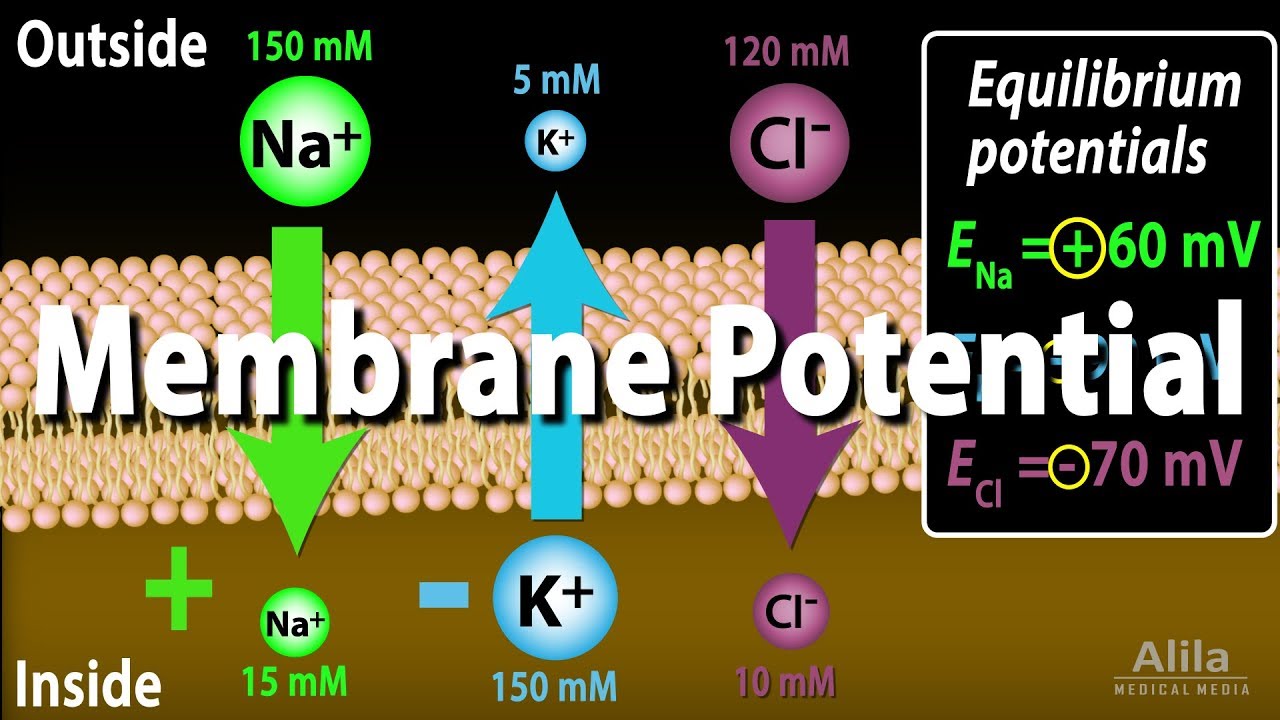
Membrane Potential, Equilibrium Potential and Resting Potential, Animation
Images related to the topicMembrane Potential, Equilibrium Potential and Resting Potential, Animation
What will happen to the membrane potential in the time that follows the closing of the channel?
What will happen to the membrane potential in the time follows the closing of the channel? It also depolarize areas further away, but not to the same degree… It returns back to the original. The shapes of some proteins are dependent on the electrical potential in the surrounding area.
How does the resting membrane potential of a typical neuron compare to the equilibrium potential calculated by the Nernst equation for potassium?
How does the resting membrane potential of a typical neuron compare to the equilibrium potential (calculated by the Nernst equation) for potassium? a. The resting membrane potential is not exactly equal to the equilibrium potential for potassium because of variation among neurons.
Related searches to Does the resting membrane potential of a neuron change if the extracellular K+ is increased?
- what is the resting membrane potential
- depolarization
- predict what will happen to the resting membrane potential if the extracellular k+ is increased
- what is an action potential
- resting membrane potential physiology
- predict what will happen to the resting membrane potential if the extracellular k is increased
- what is the resting membrane potential of a neuron
- effect of increasing extracellular potassium concentration on action potential
- the resting membrane potential is established primarily due to
- does the resting membrane potential of a neuron change if the extracellular k+ is increased
Information related to the topic Does the resting membrane potential of a neuron change if the extracellular K+ is increased?
Here are the search results of the thread Does the resting membrane potential of a neuron change if the extracellular K+ is increased? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Does the resting membrane potential of a neuron change if the extracellular K+ is increased?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.
