Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Does the hippocampus control fear?“? We answer all your questions at the website Musicbykatie.com in category: Digital Marketing Blogs You Need To Bookmark. You will find the answer right below.
Traditionally, scientists associate fear with another part of the brain, the amygdala. The hippocampus, responsible for many aspects of memory and spatial navigation, seems to play an important role in contextualizing fear, for example, by tying fearful memories to the place where they happened.Many of their studies begin with the amygdala, an almond-shaped structure that is considered the hub for fear processing in the brain. While the amygdala was once thought to be devoted exclusively to processing fear, researchers are now broadening their understanding of its role.Given a well-established role of hippocampus for memory reactivation, hippocampus is likely involved in consolidation process of fear memory. However, evidence suggests that formation of fear memory to a discrete sensory cue is hippocampus-independent.
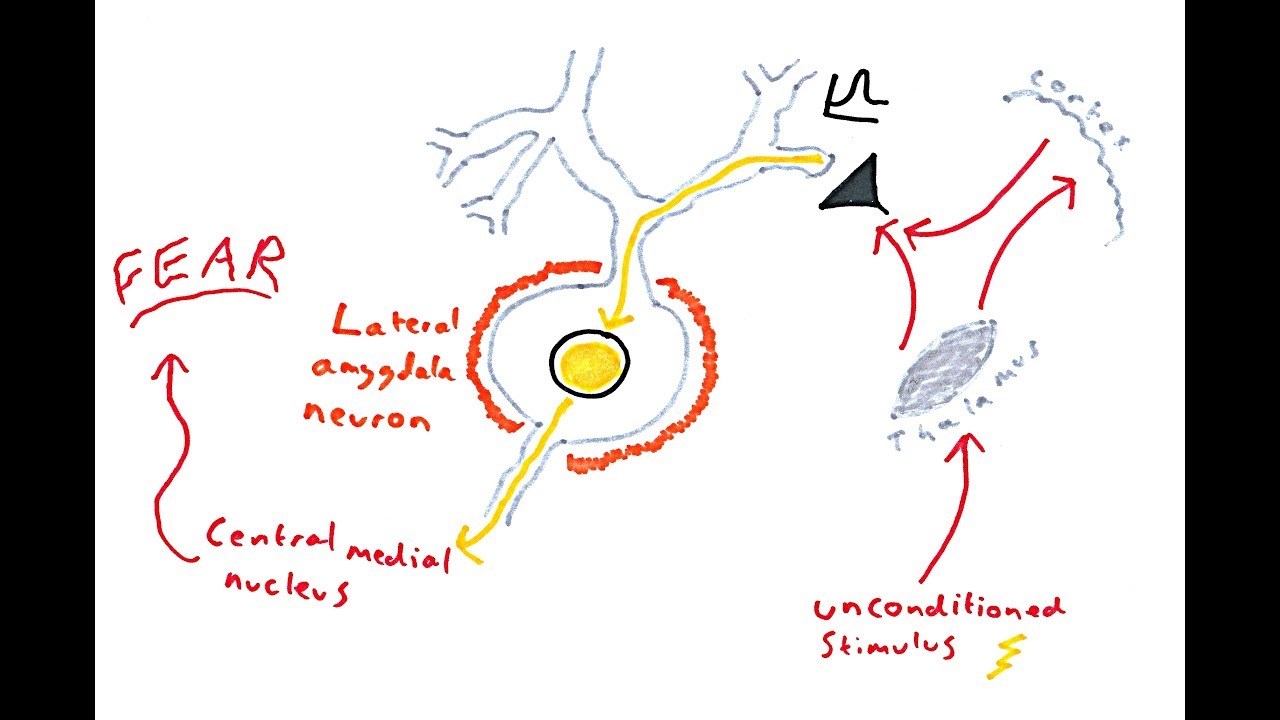
Table of Contents
What part of the brain is responsible for fear?
Many of their studies begin with the amygdala, an almond-shaped structure that is considered the hub for fear processing in the brain. While the amygdala was once thought to be devoted exclusively to processing fear, researchers are now broadening their understanding of its role.
Is the hippocampus involved in fear?
Given a well-established role of hippocampus for memory reactivation, hippocampus is likely involved in consolidation process of fear memory. However, evidence suggests that formation of fear memory to a discrete sensory cue is hippocampus-independent.
The Amygdala and Fear Conditioning
Images related to the topicThe Amygdala and Fear Conditioning

Does hippocampus control stress?
The hippocampus & stress. The hippocampus is a key brain area involved in the regulation of the stress response, exerting negative feedback on the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis (Jacobson and Sapolsky, 1991), the system within the body responsible for the release of glucocorticoid stress hormones.
What emotions does the hippocampus control?
The hippocampus, located in the medial temporal lobe and connected with the amygdala that controls emotional memory recalling and regulation (Schumacher et al., 2018); it has increased the functional connectivity with anterior cingulate or amygdala during emotional regulation and recalling of positive memory (Guzmán- …
What does the hippocampus do?
Hippocampus is a complex brain structure embedded deep into temporal lobe. It has a major role in learning and memory. It is a plastic and vulnerable structure that gets damaged by a variety of stimuli. Studies have shown that it also gets affected in a variety of neurological and psychiatric disorders.
What function does the hippocampus not control?
Hippocampus acts as an evaluation center associated with behavioral inhibition, obsessional thinking, scanning, and spatial map formation. However, the hippocampus does not actively participate in controlling behavior, once an experience is characterized.
What role does the hippocampus play in fear conditioning?
Whereas the amygdala stores the memories of stimulus related to fear, the hippocampus seems to hold the contextual stimulus about fear. The functions of the structures indicate that the amygdala and hippocampus possess complementary roles in fear conditioning.
See some more details on the topic Does the hippocampus control fear? here:
Functional emergence of the hippocampus in context fear …
The hippocampus is a part of the limbic system and is important for the formation of associative memories, such as acquiring information about the context …
The Roles of the Amygdala and the Hippocampus – DiVA portal
Behavioral data has suggested a unique role for the hippocampus in contextual fear conditioning and the model has become a major research paradigm for testing …
What Happens in the Brain When We Feel Fear – Smithsonian …
This is because the hippocampus and the frontal cortex process contextual information, and inhibitory pathways dampen the amygdala fear response …
A critical role of hippocampus for formation of remote cued …
A unique feature of fear memory is its persistence that is highly relevant to fear and anxiety-related mental disorders.
What is the role of the hippocampus and amygdala?
The amygdala is specialized for input and processing of emotion, while the hippocampus is essential for declarative or episodic memory. During emotional reactions, these two brain regions interact to translate the emotion into particular outcomes.
How do fears get conditioned?
Fear conditioning is thought to depend upon an area of the brain called the amygdala. The amygdala is involved in acquisition, storage, and expression of conditioned fear memory.
How does anxiety affect the hippocampus?
Allosteric load induced by chronic stress or anxiety causes atrophy of neurons in the hippocampus and PFC, areas associated with memory and executive function, and hypertrophy of neurons in the amygdala, a region associated with fear.
Why is the hippocampus so vulnerable?
The hippocampal formation is at the same time a very plastic brain region and a very vulnerable one to insults such as head trauma, ischemia, seizures and severe stress. Circulating glucocorticoids and endogenous excitatory amino acids acting as neurotransmitters play important roles in both aspects.
2-Minute Neuroscience: Amygdala
Images related to the topic2-Minute Neuroscience: Amygdala

Why is the hippocampus so vulnerable to stress?
The hippocampus may be especially prone to stress-induced functional and structural modifications due to its unique capacity for neurogenesis in the adult brain (22), its high concentrations of receptors for stress hormones (23), or both.
Does the amygdala or hippocampus control emotions?
The amygdala and the hippocampus are, respectively, associated with emotional processing and declarative memory (Guzmán-Vélez et al., 2016). A mature neurobiological model of emotion regulation is associated with cognitive control of emotions to prefrontal cortex areas including the amygdala and hippocampus.
What happens when hippocampus is damaged?
If one or both parts of the hippocampus are damaged by illnesses such as Alzheimer’s disease, or if they are hurt in an accident, the person can experience a loss of memory and a loss of the ability to make new, long-term memories.
How is the hippocampus activated?
The results establish that hippocampal activation in toddlers reflects past experiences, persists despite some alteration of the stimulus, and is associated with behavior. This research sheds light on early hippocampal and memory functioning and offers an approach to interrogate the neural substrates of early memory.
What part of the brain controls emotions?
The prefrontal cortex is like a control center, helping to guide our actions, and therefore, this area is also involved during emotion regulation. Both the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex are part of the emotion network.
What is the difference between hippocampus and hypothalamus?
The hypothalamus controls emotions. It also regulates your body’s temperature and controls crucial urges — such as eating or sleeping. The hippocampus sends memories to be stored in appropriate sections of the cerebrum and then recalls them when necessary.
What does the amygdala control?
The amygdala is commonly thought to form the core of a neural system for processing fearful and threatening stimuli (4), including detection of threat and activation of appropriate fear-related behaviors in response to threatening or dangerous stimuli.
When is the hippocampus most active?
Wilson and McNaughton 1994, and numerous later studies, reported that when hippocampal place cells have overlapping spatial firing fields (and therefore often fire in near-simultaneity), they tend to show correlated activity during sleep following the behavioral session.
What type of memory is fear memory?
Fear memory is the best-studied form of memory. It was thoroughly investigated in the past 60 years mostly using two classical conditioning procedures (contextual fear conditioning and fear conditioning to a tone) and one instrumental procedure (one-trial inhibitory avoidance).
What happens when you remove the hippocampus? – Sam Kean
Images related to the topicWhat happens when you remove the hippocampus? – Sam Kean
Which area of the prefrontal cortex regulates fear?
Basolateral amygdala (BLA) and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) are two areas involved in the encoding and expression of learned fear (Lauzon and Laviolette, 2010, Pape and Paré, 2010).
How does fear affect the prefrontal cortex?
The prefrontal cortex regulates the expression of fear based on previously learned information. Recently, this brain area has emerged as critical in the initial formation of fear memories, providing new avenues to study the neurobiology underlying aberrant learning in anxiety disorders.
Related searches to Does the hippocampus control fear?
- how to overcome fear
- stages of fear psychology
- types of fear responses
- does the hippocampus control learning
- does the hippocampus control fear
- what function does the hippocampus not control
- what function does the hippocampus control
- does the amygdala control fear
- what controls fear in the brain
- amygdala
- does the hippocampus control stress
- what does the hippocampus control in the brain
- what is fear
- causes of fear and anxiety
Information related to the topic Does the hippocampus control fear?
Here are the search results of the thread Does the hippocampus control fear? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Does the hippocampus control fear?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.
