Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Does potassium leach out of soil?“? We answer all your questions at the website Musicbykatie.com in category: Digital Marketing Blogs You Need To Bookmark. You will find the answer right below.
Potassium very seldom leaches from the soil. It is most abundant in its mineral form, and available forms are most often taken up by plants promptly. Erosion rarely affects potassium loss from the soil. Potassium in the grain is removed from the field during harvest.Movement of Soil Potassium
Potassium is an exception because the attraction between potassium ions and organic matter particles is relatively weak. Consequently, some potassium leaches from organic soils (peats and mucks).Both phosphorus and potassium are immobile in the soil, meaning they don’t move readily with water.
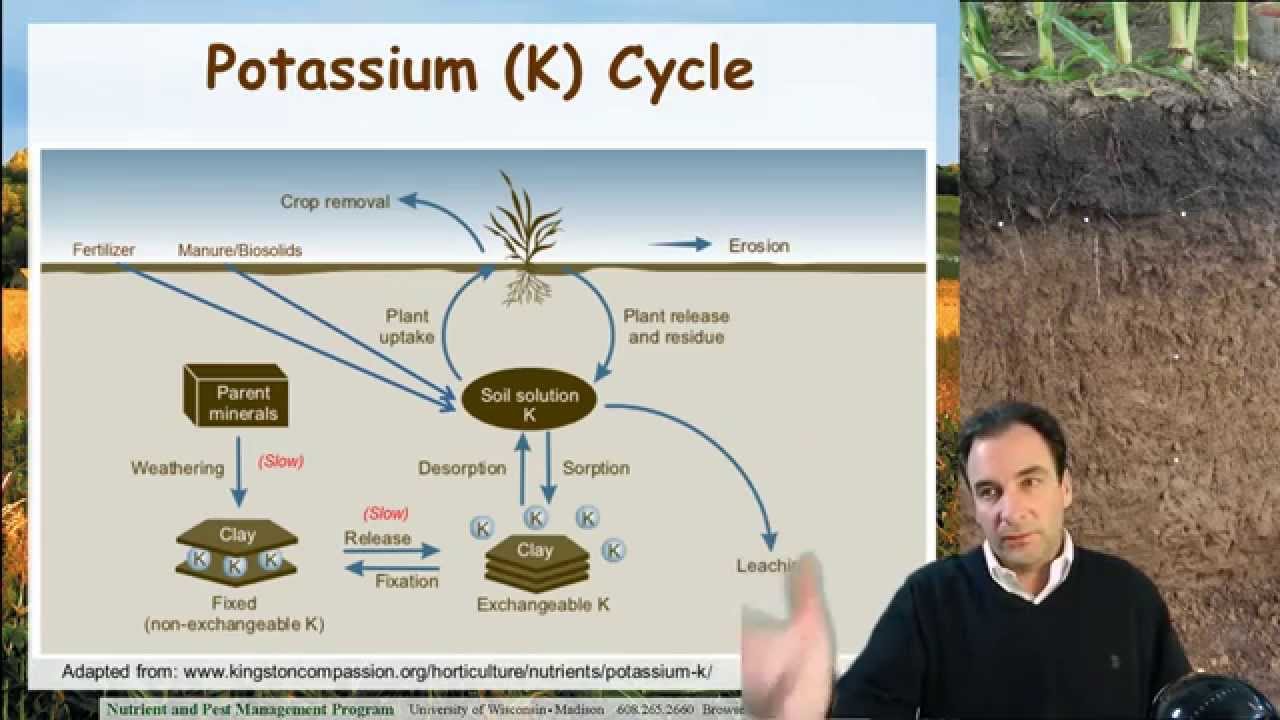
Table of Contents
Does potassium leach from soil?
Movement of Soil Potassium
Potassium is an exception because the attraction between potassium ions and organic matter particles is relatively weak. Consequently, some potassium leaches from organic soils (peats and mucks).
Does potassium stay in soil?
Both phosphorus and potassium are immobile in the soil, meaning they don’t move readily with water.
Soil Potassium, Ag Nutrient Management
Images related to the topicSoil Potassium, Ag Nutrient Management

How does potassium affect soil?
Potassium Rich Soil: Tips For Lowering Potassium Levels. Potassium is a critical nutrient that plants absorb from the soil, and from fertilizer. It increases disease resistance, helps stalks to grow upright and sturdy, improves drought tolerance, and helps plants get through the winter.
What kind of soils make potassium leaching possible?
Without K addition, K leaching mainly occurred in sandy soils at 90 mm of rainfall and in soils with greater organic matter at 225 mm of rainfall.
Is potassium prone to leaching?
considered K as the most easily leached cation, due to its displacement to the soil solution and to its percolation, especially in sandy soils.
Can you apply too much potash on a lawn?
Just like nitrogen and phosphorus, there is always a possibility of over-applying potassium to your lawn. Too much potassium does not directly harm the health of your lawn, however, it will affect the way that your soil absorbs other nutrients.
What happens if a plant has too much potassium?
The overall nutrient imbalances caused by excess potassium will limit plant growth (particularly in the stems and roots) and fruit yield. Excess potassium will affect the most mature tissues first because this is where the mineral has had the most time to accumulate.
See some more details on the topic Does potassium leach out of soil? here:
What You Need to Know About Potassium | AgWeb
Managing K leaching. K can be leached out of soil by water—up to 30 lb. or 40 lb. per acre per year—especially if the soil has a low cation …
Potassium leaching in different soils as a function of irrigation …
Potassium (K) can be easily lost by the leaching process. The objective of this study was to quantify K leaching in clayey and sandy soils under increasing …
Can I Apply Potash in Winter? – Penn State Extension
High organic, muck soils and sandy soils allow free, or exchangeable potassium to leach through the soil. Therefore, avoid winter or fall potash …
Too Much Potassium – How To Treat High Potassium In Soils
Potassium is a critical nutrient that plants absorb from the soil, and from fertilizer. A little extra potassium generally isn’t cause for …
Do houseplants like potassium?
Potassium is super essential for catalyzing enzymes in a plant—at least 60 of them—which again, is important for protein synthesis and ultimately plant growth. Potassium also regulates the opening and closing of the stomata, or plant pores. This is where the CO2, O2 and water vapor is exchanged.
Is potassium good for all plants?
While the role of potassium is vital to all plants, it is especially necessary for food crops. Research has shown potassium: Improves water use efficiency. Increases resistance to diseases and insects.
How is potassium used in soil?
Plants take up potassium as the K+ ion. Over time “slowly available K” is released replacing exchangeable K; however, plants cannot use much of this form of K in a single growing season. K has a role in the plant physiology and chemistry with movement of water, nutrients, and carbohydrates within the plant.
What does potassium do in fertilizer?
Potassium is the third key nutrient of commercial fertilizers. It helps strengthen plants’ abilities to resist disease and plays an important role in increasing crop yields and overall quality. Potassium also protects the plant when the weather is cold or dry, strengthening its root system and preventing wilt.
Why is my soil high in potassium?
If the test shows a high concentration of potassium, it could indicate dense clay soil, which traps the mineral and allows it to build to highly concentrated levels. The results could also mean that the fertilizer you are using contains too much of it.
What Happens When Plants Get Too Much Potassium?
Images related to the topicWhat Happens When Plants Get Too Much Potassium?

How do you fix potassium deficiency in soil?
To correct a deficiency, spread organic mulch beneath plants and apply potassium fertilizer, preferably slow-release forms such as potassium silicate or sulfur- or polymer-coated potassium products. Potassium sulfate may be used, and potassium will be held by organic matter and clay particles.
What causes low potassium in soil?
Potassium deficiency can be caused by soil pH, extreme liming or calcium rich areas of fields, lack of soil oxygen or true soil deficiency. Foliar application of potassium can help in cases where deficiencies are caused by reasons other than true soil deficiency.
How does phosphorus get into soil?
Weathering, Precipitation, and Dissolution. Soil contains minerals that are rich in phosphorus. These minerals are classified into primary and secondary minerals. Minerals break down over time (a process referred to as weathering) and release phosphorus in the soil solution for plant uptake.
Which nutrients leach from the soil?
The three most commonly applied nutrients are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and potassium (K). Of these nutrients, nitrogen is the most likely to be leached from the soil.
How do you prevent soil leaching?
Use crop rotation to add nitrogen and organic matter to your soils. Crop rotations also reduce insects and diseases and improve yields. Use cover crops to add nitrogen as well as organic matter.
Does phosphorus leach in soil?
Phosphorus does not readily leach out of the root zone; potential for P-loss is mainly associated with erosion and runoff. Soils and sites that are most prone to erosion and runoff, or are in close proximity to streams, lakes and other water bodies need to be closely managed to avoid P loss.
Can potassium burn grass?
Potassium fertilizer should be applied when the turfgrass is actively growing. It is best to apply in spring when the turfgrass is fully out of dormancy and has been mowed several times. Similar to concerns one would have with some nitrogen fertilizers, potassium can also cause leaf burn when applied.
When should I put potassium on my lawn?
Fall is a good time to apply higher levels of potassium so the grass can better withstand the ravages of winter weather. Frequently, fall-winter lawn fertilizer formulas emphasize nitrogen values but pay little attention to potassium values.
How do you apply potash to soil?
Potash doesn’t move in soil so if you want to sprinkle it into the root zone, you have to till it into the root zone. On average, you should have 1/4 to 1/3 pound of potassium sulfate or potassium chloride per 100 square feet. To increase the potassium content in your soil, add wood ash to your compost heap.
Is potassium good for growing tomatoes?
For good yield and fruit quality, tomatoes need an ample supply of potassium (potash) which can be supplied with fertilizer, wood ashes and organic matter. 4. Maintain proper soil pH. This is important for optimum nutrient availability and health of many beneficial soil organisms.
Soil potassium and plant nutrition
Images related to the topicSoil potassium and plant nutrition

Does potassium promote root growth?
Potassium promotes increased root growth and thicker cell walls. Turfgrasses require potassium in nearly the same amount as nitrogen, especially in sandy soils where both can readily leach out.”
Can tomato plants have too much potassium?
Too much potassium in the soil can stunt growth and lead to chlorosis, a condition where older growth is yellow and leaves show red veins. Tomatoes need high levels of potassium in their soil. Excess potassium in a plant’s soil will result in a low yield and an overgrown plant.
Related searches to Does potassium leach out of soil?
- how does potassium get into soil besides fertilizer
- is potassium mobile in plants
- potassium cycle
- is phosphorus mobile in soil
- does potassium leach out of soil or water
- does potassium leach out of soil for plants
- potassium deficiency in plants
- does potassium leach out of soil in the garden
- how does phosphorus get into soil
- potassium leaching in soil
- what does potassium do for plants
- does potassium leach out of soil in the soil
Information related to the topic Does potassium leach out of soil?
Here are the search results of the thread Does potassium leach out of soil? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Does potassium leach out of soil?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.
