Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Do plants engage in homeostasis?“? We answer all your questions at the website Musicbykatie.com in category: Digital Marketing Blogs You Need To Bookmark. You will find the answer right below.
Collectively, these data indicate that plants must integrate nutritional status with immunity to maintain symbiotic homeostasis.Plants are constantly exposed to microbes: Pathogens that cause disease, commensals that cause no harm or benefit, and mutualists that promote plant growth or help fend off pathogens. For example, most land plants can form positive relationships with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to improve nutrient uptake.Researchers discover how plants distinguish beneficial from harmful microbes. Legume plants fix atmospheric nitrogen with the help of symbiotic bacteria, called Rhizobia, which colonize their roots. Therefore, plants have to be able to precisely recognize their symbiont to avoid infection by pathogenic microbes.

Table of Contents
How do plants balance microbial friends and foes?
Plants are constantly exposed to microbes: Pathogens that cause disease, commensals that cause no harm or benefit, and mutualists that promote plant growth or help fend off pathogens. For example, most land plants can form positive relationships with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to improve nutrient uptake.
How plants distinguish beneficial from harmful microbes?
Researchers discover how plants distinguish beneficial from harmful microbes. Legume plants fix atmospheric nitrogen with the help of symbiotic bacteria, called Rhizobia, which colonize their roots. Therefore, plants have to be able to precisely recognize their symbiont to avoid infection by pathogenic microbes.
Chapter 14.5: Homeostasis in Plants
Images related to the topicChapter 14.5: Homeostasis in Plants

How do bacteria interaction with bacteria affect bacteria interaction with plants?
Interactions with bacteria can induce two types of plant defence responses that help protect against further infection. Systemic acquired resistance (SAR) is a specific response that triggers both a local increase in phytohormone accumulation and the formation of phloem mobile signal.
How do plants discern friends from foes?
Plants discern friends by the flagellin epitope variation
Both symbiotic and pathogenic microorganisms generate a diversity of MAMPs. The study of MAMP-induced immune responses has so far focused on a handful of epitope variants produced by pathogenic and beneficial bacteria.
Which of the following human diseases has almost been eradicated?
That power has so far eradicated two infectious diseases: smallpox and rinderpest. We are also getting closer to eradicating polio and Guinea worm disease.
How do plants engage with beneficial bacteria while at the same time restricting pathogens?
In rhizobia-legume interactions, plants recognize specific microbial chemical signals, which leads to mutualistic symbiosis. Plant recognition of pathogens can lead to a robust immune response and restriction of microbial growth.
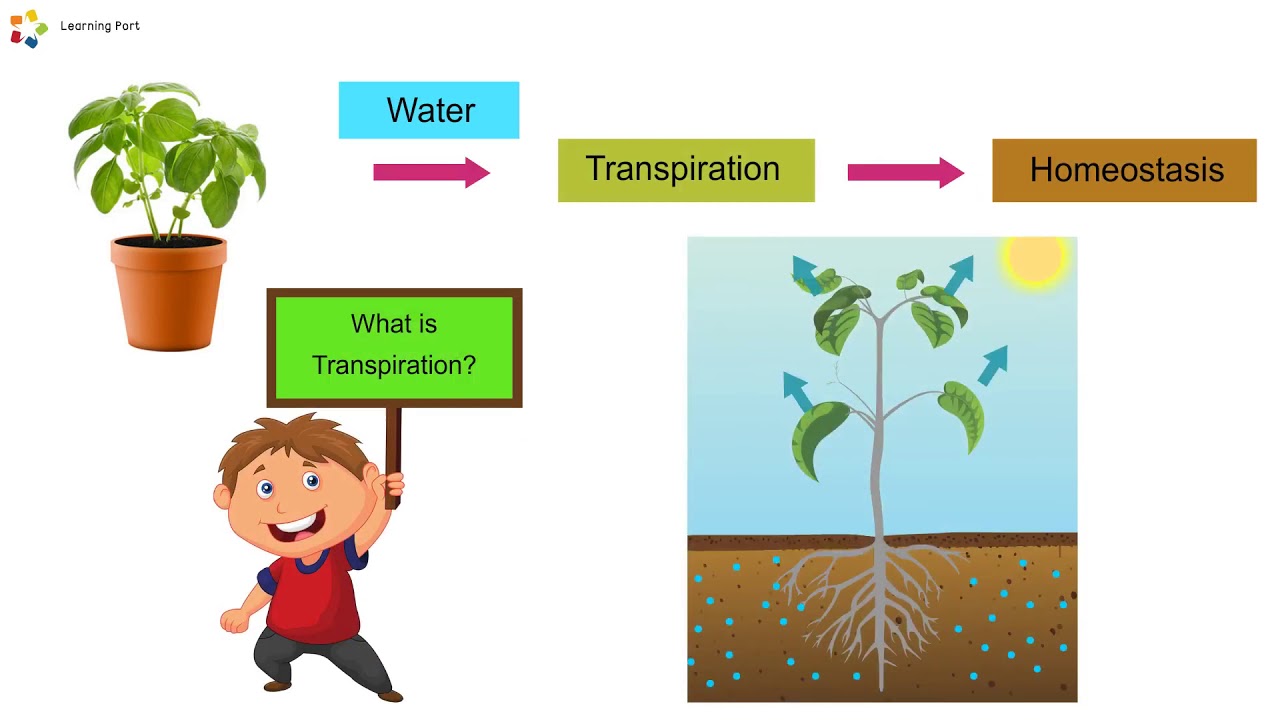
Homeostasis in Plants
Images related to the topicHomeostasis in Plants
See some more details on the topic Do plants engage in homeostasis? here:
How Do Plants Engage With Beneficial Microorganisms While …
Maintaining Symbiotic Homeostasis: How Do Plants Engage With Beneficial Microorganisms While at the Same Time Restricting Pathogens? Mol Plant Microbe Interact.
Homeostasis in Plants – Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com
Homeostasis is the ability to maintain a stable internal state despite external changes in the world. Plants absorb water from the soil and …
(PDF) Maintaining Symbiotic Homeostasis: How Do Plants …
Plants have an innate immune system to fight off potential invaders that is based on the perception of nonself or modified-self molecules. Microbe-associated …
How do plants balance microbial friends and foes? – Phys.org
Plants first use metabolite compounds like antimicrobials and chemical signals to recruit beneficial organisms and restrict pathogens, but not …
How do plants interact with bacteria?
The bacteria that provide some benefit to plants [i.e. plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB)] are of three general types: (i) those that form a symbiotic relationship, which involves formation of specialized structures or nodules on host plant roots, (ii) those that are endophytic and colonize the inner tissues of the …
How do plant and microbes interact in the soil?
Soil microbial communities contain a diversity of plant-antagonistic and plant-beneficial microbes, and plants respond to these soil communities in species-specific ways (Bever 1994). These species-specific responses help set the stage for soil microbes to influence plant community composition (Bever et al.
What is the association between microbes and plants?
Microorganisms have a range of direct effects on plants through, e.g., manipulation of hormone signaling and protection against pathogens. Plants communicate with the microorganisms through metabolites exuded by the roots.
What diseases no longer exist?
- So far, only two diseases have been successfully eradicated—one specifically affecting humans (smallpox), and one affecting a wide range of ruminants (rinderpest).
- Smallpox is the first disease, and so far the only infectious disease of humans, to be eradicated by deliberate intervention.
What are indigenous bacteria?
Indigenous microorganisms do not contain a single culture of beneficial microorganisms but a mixture of different beneficial microorganisms; it is a village of good bacteria that are living together in harmony with the rest of nature.
Homeostasis and Negative/Positive Feedback
Images related to the topicHomeostasis and Negative/Positive Feedback

Which disease is completely eradicated from India by vaccination?
Smallpox is an acute contagious disease caused by the variola virus, a member of the Orthopoxvirus family. It is completely eradicated from India in 1977 when A WHO International Commission comprising experts in epidemiology and infectious diseases from 16 countries carefully reviewed the data.
What are beneficial microbes?
Beneficial microorganisms are naturally occurring bacteria, fungi, and other microbes that play a crucial role in plant productivity and health. Two types of beneficial microorganisms, mycorrhizal fungi and nitrogen-fixing bacteria , are considered beneficial to plant health.
Related searches to Do plants engage in homeostasis?
- homeostasis in plants pdf
- unanswered questions about plants
- plant immunity
- prr in plants
- do plants maintain homeostasis
- do plants have homeostasis
- homeostasis in plants ppt
- do plants do homeostasis
- how do animals maintain homeostasis
- plant microbe interaction research paper
Information related to the topic Do plants engage in homeostasis?
Here are the search results of the thread Do plants engage in homeostasis? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Do plants engage in homeostasis?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.
