Table of Contents
What is the reaction of alpha beta unsaturated ketone?
You’re right to be curious about this. It’s a pretty interesting and versatile reaction. The key to understanding it is to remember that alpha, beta-unsaturated ketones have a special combination of features.
First, they have a carbonyl group (C=O) which makes them reactive. Second, the double bond between the alpha and beta carbons (the carbon next to the carbonyl and the one after it) gives them a special kind of reactivity. This double bond can be attacked by different molecules, leading to a variety of interesting reactions.
Now, let’s look at the reaction you mentioned. In this case, the alpha, beta-unsaturated ketone is formed by reacting DHA (dehydroascorbic acid) with an aromatic aldehyde. The reaction of this alpha, beta-unsaturated ketone with o-ATP (o-aminophenyl thiourea) is really cool because it leads to two different products: dihydro-1,5-benzothiazepines and dihydrobenzothiazines. These are both cyclic compounds with nitrogen and sulfur atoms, and their formation tells us that the alpha, beta-unsaturated ketone can react in multiple ways.
Here’s the breakdown of what’s happening:
Step 1: Formation of the alpha, beta-unsaturated ketone: DHA, which is a reducing agent, reacts with an aromatic aldehyde to form the alpha, beta-unsaturated ketone. This reaction involves the loss of a water molecule.
Step 2: Reaction of the alpha, beta-unsaturated ketone with o-ATP: The newly formed alpha, beta-unsaturated ketone is then attacked by o-ATP. The o-ATP can attack at either the carbonyl group or the double bond. If it attacks the carbonyl group, you get the dihydro-1,5-benzothiazepine product. If it attacks the double bond, you get the dihydrobenzothiazine product.
What’s important to understand is that the reaction of alpha, beta-unsaturated ketones is not just about one particular product. Instead, it’s about a variety of possibilities. Depending on the conditions (the exact structure of the ketone, the other reactants, the temperature, etc.) you can get different products.
In short, the reaction of alpha, beta-unsaturated ketones can be a really creative and versatile way to make different kinds of molecules. This is why it’s important to understand the key features of these compounds and the factors that affect their reactivity.
What is the hydrogenation of alpha beta unsaturated ketones?
You see, alpha beta unsaturated ketones have a special structure. They have a carbon-carbon double bond right next to a carbonyl group. This makes them unique and reactive.
When we hydrogenate these ketones, we’re basically adding hydrogen atoms. But here’s the catch: we can get two different products depending on where the hydrogen atoms go!
First Scenario: The hydrogen atoms can add to the carbon-carbon double bond. This gives us a saturated ketone.
Second Scenario: The hydrogen atoms can add to the carbonyl group. This gives us an unsaturated alcohol.
So, the hydrogenation of alpha beta unsaturated ketones is a bit like choosing a path – you can either saturate the ketone or make an alcohol. It all depends on how the hydrogen atoms decide to attach themselves!
Here’s a little more detail on the hydrogenation of alpha beta unsaturated ketones. The key to understanding this reaction is to think about the catalyst.
Catalysts play a big role in hydrogenation. The type of catalyst we use can determine whether the hydrogen atoms add to the carbon-carbon double bond or the carbonyl group.
For example, using palladium on carbon as a catalyst usually leads to the hydrogenation of the carbon-carbon double bond, giving you a saturated ketone.
But, if you use Raney nickel as a catalyst, you’re more likely to get hydrogenation of the carbonyl group, resulting in an unsaturated alcohol.
So, the hydrogenation of alpha beta unsaturated ketones is a versatile reaction that can lead to different products depending on the catalyst. It’s a useful reaction that can be used to create a variety of important compounds.
What are the examples of enone?
The simplest example is methyl vinyl ketone (butenone, CH2=CHCOCH3).
You can make enones using a couple of handy reactions: aldol condensation or Knoevenagel condensation.
Enones are pretty important in the chemical world, and some are even made on a large scale. A few examples made by reacting acetone with itself are mesityl oxide (a dimer of acetone), and phorone and isophorone (both trimers of acetone).
Enones are fascinating molecules! They’re known for their reactivity, and that’s because they have a double bond and a carbonyl group (C=O) right next to each other. This special arrangement makes them ideal for all sorts of chemical reactions, which is why they’re so useful in organic chemistry.
Think of it like this: the double bond is like a hungry wolf, and the carbonyl group is like a juicy lamb. They’re both attracted to each other, and they can easily react with other molecules.
That’s why enones are popular building blocks for making all sorts of things, like pharmaceuticals, dyes, and pesticides.
I hope this gives you a better picture of what enones are and how they’re made!
Why is it called alpha beta unsaturated?
Let’s break it down:
Unsaturated: In organic chemistry, “unsaturated” refers to molecules that have double or triple bonds between carbon atoms. Think of it like this: a single bond is like a road with one lane, while a double bond is a road with two lanes. Double and triple bonds create more opportunities for reactions, making the molecule more “reactive” or “unsaturated”.
Alpha and Beta: These labels are used to describe the positions of carbon atoms relative to a functional group, like a carbonyl group (C=O). The carbon directly attached to the carbonyl group is called the alpha carbon, and the next carbon over is called the beta carbon.
So, when we say alpha beta unsaturated, it means there’s a double bond between the alpha carbon and the beta carbon near a carbonyl group. This arrangement is common in many important organic molecules, and it has some interesting properties.
Here’s a visual example:
Imagine a molecule with a carbonyl group (C=O). The carbon atom directly attached to the oxygen atom of the carbonyl group is the alpha carbon. The carbon atom next to the alpha carbon is the beta carbon. If there’s a double bond between the alpha carbon and the beta carbon, then we call the molecule alpha beta unsaturated.
Think of it like this: The double bond between the alpha and beta carbons is like a “bottleneck” that can make the molecule more reactive. This reactivity can be useful in a variety of chemical reactions, which is why alpha beta unsaturated molecules are so important in organic chemistry.
Let me know if you have any other questions about organic chemistry! I’m happy to help you understand the fascinating world of molecules.
Does hydrogenation affect ketones?
Let’s break down how it works. Hydrogenation involves adding hydrogen atoms (H2) to a molecule. When we talk about ketones, we’re dealing with molecules that have a carbonyl group (C=O). In asymmetric hydrogenation, we use a special catalyst that helps the hydrogen atoms add to the ketone in a way that favors one specific direction. This is where the “asymmetric” part comes in. It’s like choosing a specific side of the molecule for the hydrogen atoms to land on.
The result of this process is a secondary alcohol that’s not just any alcohol; it’s optically active, meaning it rotates polarized light. Think of it like a molecule that has a specific “handedness.” This “handedness” is important because different molecules can interact differently with biological systems, and this is why optically active secondary alcohols are so useful in making medicines, fragrances, and agricultural chemicals.
Scheme 1, which you mentioned, likely shows a visual representation of this process. It might include the ketone, the catalyst, and the resulting optically active secondary alcohol.
What is the product of the hydrogenation of ketones?
Let’s break down what happens during this reaction. Ketones, a type of organic compound, have a characteristic carbonyl group (C=O). This group contains a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom. When hydrogen is added to the ketone, the double bond breaks, and the hydrogen atoms attach to both the carbon and the oxygen atoms. This converts the carbonyl group into a hydroxyl group (OH), which is the defining characteristic of alcohols.
This reaction is a reduction reaction, meaning that the ketone gains electrons from the hydrogen molecule. Think of it like this: the ketone “wants” to have more electrons, and the hydrogen provides them. This change in electron count is what transforms the ketone into an alcohol.
For example, the hydrogenation of propanone (also known as acetone), a common ketone, produces propan-2-ol (also known as isopropanol), a familiar alcohol used as a disinfectant and rubbing alcohol. The reaction can be represented by the following equation:
CH3COCH3 + H2 → CH3CH(OH)CH3
Here, propanone (CH3COCH3) reacts with hydrogen (H2) to form propan-2-ol (CH3CH(OH)CH3).
In summary, hydrogenating a ketone is a straightforward way to convert it into an alcohol. This reaction is crucial in organic chemistry, as it allows us to create alcohols from ketones, which are valuable starting materials for synthesizing a wide range of organic compounds.
What is selective hydrogenation of unsaturated ketones?
While achieving highly chemoselective 1,4-hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated ketones has been a significant challenge, researchers have made remarkable progress. Traditionally, this reaction was primarily achieved via transfer hydrogenation utilizing precious metals. Transfer hydrogenation involves using a hydrogen donor molecule, such as isopropanol or formic acid, to transfer hydrogen to the unsaturated ketone. Precious metals like palladium, platinum, and ruthenium are often used as catalysts, showcasing excellent activity and selectivity.
However, the use of precious metals poses several drawbacks. They are expensive, scarce, and can be environmentally problematic. This has fueled an ongoing search for more sustainable and cost-effective alternatives. Recent research has focused on developing catalysts based on abundant and less expensive metals like iron, nickel, and copper. These catalysts, often combined with suitable ligands, have shown promising results, offering a more sustainable approach to selective 1,4-hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated ketones.
For instance, researchers have explored using iron-based catalysts. These catalysts, often combined with specific ligands, have demonstrated remarkable activity and selectivity in the 1,4-hydrogenation of various α,β-unsaturated ketones. The use of iron catalysts offers a more environmentally friendly and cost-effective alternative to traditional precious metal catalysts.
Is enone a functional group?
Enones, also known as α,β unsaturated ketones, are a special type of molecule. They’re formed when a ketone group is directly attached to a carbon-carbon double bond. This arrangement creates a unique chemical environment where the ketone and alkene parts of the molecule influence each other, leading to interesting reactivity.
But is it a functional group? Absolutely! A functional group is a specific atom or group of atoms within a molecule that is responsible for its characteristic chemical reactions. Enones fit this definition perfectly, as the ketone and alkene combination gives them a distinct set of chemical properties.
Think of it like this: Imagine a molecule as a puzzle. Each piece of the puzzle has its own shape and properties. A functional group is like a special piece that gives the entire puzzle its unique characteristics. In the case of enones, the ketone and alkene pieces together are the “special piece” that defines their reactivity.
For example, enones are known for undergoing reactions like Michael addition, where a nucleophile adds to the β-carbon of the enone. This specific reaction is due to the combined influence of the ketone and alkene, and it wouldn’t happen without that unique functional group.
So, when you see the term enone, know that you’re looking at a molecule with a distinct functional group, ready to exhibit its unique chemical behavior.
See more here: What Is The Hydrogenation Of Alpha Beta Unsaturated Ketones? | Alpha Beta Unsaturated Ketone Reduction
See more new information: musicbykatie.com
Alpha Beta Unsaturated Ketone Reduction: Strategies And Applications
Hey there, chemistry enthusiasts! Today, we’re diving deep into the fascinating world of alpha beta unsaturated ketone reduction. This reaction is a fundamental concept in organic chemistry, and understanding it is crucial for anyone who wants to grasp the intricacies of carbonyl chemistry.
Let’s break it down step by step, starting with the basics.
What is an Alpha Beta Unsaturated Ketone?
An alpha beta unsaturated ketone is a molecule with a carbonyl group (C=O) directly attached to a carbon-carbon double bond. The carbon atom next to the carbonyl group is called the alpha carbon, and the carbon atom next to the alpha carbon is the beta carbon. So, the double bond is between the alpha and beta carbons, hence the name.
Think of it like this:
Ketone: The heart of the molecule with its characteristic carbonyl group.
Double bond: A nearby ally, adding a twist to the reactivity.
This combination gives rise to a unique reactivity pattern. The carbonyl group is electron-withdrawing, making the beta carbon more susceptible to attack by nucleophiles.
The Magic of Reduction
Now, reduction refers to the gain of electrons or the loss of oxygen. In the context of organic chemistry, we often use reducing agents to transform a carbonyl group into an alcohol or even a hydrocarbon.
When we talk about alpha beta unsaturated ketone reduction, we’re specifically aiming to convert the double bond into a single bond while also reducing the carbonyl group. This can lead to a range of products, depending on the reducing agent and the reaction conditions.
Key Players in the Reaction
There are two main categories of reducing agents commonly used in alpha beta unsaturated ketone reduction:
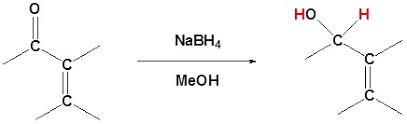
Hydride Reducing Agents: These are reagents that donate a hydride ion (H-), like sodium borohydride (NaBH4) and lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4). They are powerful reducing agents that can reduce both the carbonyl group and the double bond.
Catalytic Hydrogenation: This method utilizes hydrogen gas (H2) in the presence of a metal catalyst, such as palladium (Pd) or platinum (Pt). This approach allows for selective reduction of the double bond without affecting the carbonyl group.
Exploring the Possibilities
Depending on the reducing agent and the reaction conditions, alpha beta unsaturated ketone reduction can yield different products:
1,4-Addition: This occurs when the hydride ion attacks the beta carbon of the double bond. This is favored by bulky reducing agents or polar solvents. The product is a saturated ketone.
1,2-Addition: This happens when the hydride ion attacks the carbonyl carbon directly. This is often favored in nonpolar solvents or with less bulky reducing agents. This leads to a saturated alcohol.
The Importance of Selectivity
Choosing the right reducing agent and reaction conditions is crucial for achieving the desired outcome. For example, if we want to selectively reduce the double bond without affecting the carbonyl group, we would choose a catalytic hydrogenation method. On the other hand, if we want to reduce both the carbonyl group and the double bond, we would use a strong hydride reducing agent like LiAlH4.
Beyond the Basics
The study of alpha beta unsaturated ketone reduction extends beyond these fundamental concepts. The reaction can be influenced by factors like:
Stereochemistry: The configuration of the double bond and the presence of chiral centers can impact the stereochemical outcome of the reduction.
The nature of the carbonyl group: The presence of electron-donating or electron-withdrawing groups on the carbonyl group can affect its reactivity and the products formed.
Solvent effects: The solvent used can influence the rate and selectivity of the reaction.
Real-World Applications
Alpha beta unsaturated ketone reduction is a powerful tool with diverse applications in organic synthesis and medicinal chemistry:
Synthesis of Natural Products: This reaction is used extensively in the synthesis of complex natural products, such as steroids and terpenes.
Drug Discovery: The selective reduction of alpha beta unsaturated ketones is often used in the design and synthesis of new drug candidates.
FAQs
#What are the main factors that influence the selectivity of alpha beta unsaturated ketone reduction?
The main factors influencing selectivity include the nature of the reducing agent, the solvent used, and the presence of electron-withdrawing or electron-donating groups on the carbonyl group.
#What is the difference between 1,2-addition and 1,4-addition in alpha beta unsaturated ketone reduction?
1,2-Addition occurs when the hydride ion attacks the carbonyl carbon directly, resulting in a saturated alcohol. 1,4-Addition involves the hydride ion attacking the beta carbon of the double bond, leading to a saturated ketone.
#What are some common examples of alpha beta unsaturated ketones?
Some examples include methyl vinyl ketone, cyclohexenone, and testosterone.
#What is the role of catalysts in alpha beta unsaturated ketone reduction?
Catalysts, like palladium and platinum, are used in catalytic hydrogenation to facilitate the addition of hydrogen gas to the double bond. They provide a surface for the reaction to occur, increasing the rate of the process.
#Can alpha beta unsaturated ketone reduction be used to create new chiral centers?
Yes, depending on the reducing agent and reaction conditions, alpha beta unsaturated ketone reduction can create new chiral centers, leading to a variety of stereoisomers.
#Why is alpha beta unsaturated ketone reduction important in organic synthesis?
Alpha beta unsaturated ketone reduction is an essential tool in organic synthesis as it provides a versatile method for transforming carbonyl groups and double bonds into different functional groups, enabling the synthesis of a wide array of molecules with diverse functionalities.
We’ve covered a lot of ground today, exploring the intricacies of alpha beta unsaturated ketone reduction. This reaction is a fundamental concept in organic chemistry with a wide range of applications. Remember, understanding the factors that influence the reaction, choosing the right reducing agent, and controlling reaction conditions are key to achieving your desired outcome.
Keep experimenting, keep learning, and happy chemistry!
1,4-Reduction of α,β-unsaturated compounds – Organic
A chiral bisphosphine dioxide catalyzes an asymmetric conjugate reduction of acyclic β,β-disubstituted α,β-unsaturated ketones with trichlorosilane to provide saturated ketones with high enantioselectivities. Organic Chemistry Portal
Chemoselective Luche-Type Reduction of α,β-Unsaturated
The chemoselective reduction of α,β-unsaturated ketones by use of an economic and readily available Mg catalyst has been developed. Excellent yields for a ACS Publications
Highly Selective Reduction of α, β‐Unsaturated
An efficient and green protocol for highly selective reduction of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes and ketones at room Chemistry Europe
Chemoselective Conjugate Reduction of α,β-Unsaturated
Now we have found that a variety of α,β-unsaturated ketones, even without other electron-withdrawing functional groups, could be reduced on the alkenic double ACS Publications
Electrochemical 1,4-reduction of α,β-unsaturated ketones with
A sustainable, chemoselective 1,4-reduction of α,β-unsaturated ketones by means of an electrochemical method is presented, wherein the extremely inexpensive RSC Publishing
Chemoselective reduction of α,β-unsaturated ketones to allylic
Herein, we describe an ever more expedient, green and general method for the chemoselective reductions of exo- and endo-α,β-unsaturated cycloketones and acyclic RSC Publishing
Chemoselective and metal-free reduction of α,β
General procedure for chemoselective reduction of (hetero)arylidene acetones 2a–o. A 25 mL round-bottom flask equipped with a stir bar and a condenser was charged with α,β-unsaturated ketone 2 (0.3 mmol), RSC Publishing
1,2- Versus 1,4-Asymmetric Reduction of Ketones | SpringerLink
Reduction of α,β-unsaturated ketones generally can give rise to a variety of products, of which chiral allylic alcohols (1,2-reduction) and saturated ketones (1,4 springer.com
Synthesis of α,β-unsaturated ketones through nickel-catalysed
Transition metal-catalysed hydroacylation of alkynes using aldehydes is an atom-economical route to access α,β-unsaturated ketones, but typically requires Nature
Alpha,beta-Unsaturated Ketone – an overview
Certain α,β-unsaturated aldehydes and ketones can form pyrazolines in the presence of hydrazine which on heating yield cyclopropanes; 73 nevertheless, some α,β ScienceDirect
14.01 Alpha,Beta-Unsaturated Carbonyl Compounds
Direct 1,2 Addition In Alpha Beta Unsaturated Ketones Aldehydes And Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Reduction Of Unsaturated Ketones
Aldehydes And Ketones
Nucleophilic Addition Reaction Mechanism, Grignard Reagent, Nabh4, Lialh4, Imine, Enamine, Reduction
|Reduction Of Alpha-Beta Unsaturated Aldehyde And Ketones Lec04|#Lialh4#Nabh4#Chemoselectivity#9-Bbn
Birch Reduction On Α,Β-Unsaturated Carbonyls (Ketones): Basic Idea, Reaction Mechanism \U0026 Selectivity
Alpha Beta Unsaturated Carbonyl Additions
Link to this article: alpha beta unsaturated ketone reduction.
See more articles in the same category here: https://musicbykatie.com/wiki-how/
