Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Does pulmonary fibrosis cause mucus?“? We answer all your questions at the website Musicbykatie.com in category: Digital Marketing Blogs You Need To Bookmark. You will find the answer right below.
With pulmonary fibrosis your cough may be dry and tickly, or it can be productive of mucus.One of the possible symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis is a frequent cough which does not seem to go away. The cough related to pulmonary fibrosis is dry (does not produce phlegm) and is a common cause of great frustration.What is cystic fibrosis (CF)? Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic (inherited) disease that causes sticky, thick mucus to build up in organs, including your lungs and pancreas. If you don’t have CF, the mucus that lines organs and body cavities, such as your lungs and nose, is slippery and watery.
- feeling more severely out of breath.
- reducing lung function making breathing harder.
- having frequent flare-ups.
- finding it difficult to maintain a healthy body weight due to loss of appetite.
- feeling more anxious and depressed.
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- A dry cough.
- Fatigue.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Aching muscles and joints.
- Widening and rounding of the tips of the fingers or toes (clubbing)

Table of Contents
Does pulmonary fibrosis cause excess mucus?
One of the possible symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis is a frequent cough which does not seem to go away. The cough related to pulmonary fibrosis is dry (does not produce phlegm) and is a common cause of great frustration.
What disease causes excessive mucus production?
What is cystic fibrosis (CF)? Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic (inherited) disease that causes sticky, thick mucus to build up in organs, including your lungs and pancreas. If you don’t have CF, the mucus that lines organs and body cavities, such as your lungs and nose, is slippery and watery.
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: What’s the cause of my cough? Part 1
Images related to the topicIdiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: What’s the cause of my cough? Part 1

What are the signs that pulmonary fibrosis is getting worse?
- feeling more severely out of breath.
- reducing lung function making breathing harder.
- having frequent flare-ups.
- finding it difficult to maintain a healthy body weight due to loss of appetite.
- feeling more anxious and depressed.
What are the first signs of pulmonary fibrosis?
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- A dry cough.
- Fatigue.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Aching muscles and joints.
- Widening and rounding of the tips of the fingers or toes (clubbing)
How do I stop excessive mucus production?
- Hydrate more. Drink more water. …
- Use a humidifier. …
- Check filters on heating and cooling systems. …
- Use a nasal saline spray. …
- Gargle with salt water. …
- Use eucalyptus. …
- Use over-the-counter medication.
How do you know if your lungs are filled with mucus?
According to Medical News Today2, common symptoms of mucus build up in your lungs may include: Wheezing. Difficulty Sleeping. Sore Throat.
Why am I full of mucus all the time?
Excess mucus production can also result from certain lifestyle and environmental factors, such as: a dry indoor environment. low consumption of water and other fluids. high consumption of fluids that can lead to fluid loss, such as coffee, tea, and alcohol.
See some more details on the topic Does pulmonary fibrosis cause mucus? here:
Managing your cough – Life With Pulmonary Fibrosis
One of the possible symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis is a frequent cough which does not seem to go away. The cough related to pulmonary fibrosis is dry (does …
Dealing with Phlegm. – Pulmonary Fibrosis News
In the literature there are numerous mentions of a “dry cough” being symptomatic of PF, but not much about excessive phlegm. I am one of those diagnosed with …
Understanding Mucus in Your Lungs
It is a common symptom in chronic lung diseases such as COPD (including chronic bronchitis and emphysema), cystic fibrosis, bronchiectasis, …
Mucus, cough and chronic lung disease – ScienceDaily
But in certain types of chronic lung disease, such as cystic fibrosis or COPD, the mucus remains on the airway surface.
Why do I have an overproduction of mucus?
Conditions that can contribute to excess mucus include allergies, asthma, and bronchitis. Smoking and conditions like COPD and cystic fibrosis can also cause this symptom. Your doctor may order a sputum test to find the cause of your excess mucus.
Why does mucus keep coming back?
Postnasal drip is usually due to certain changes in the environment or the body. One of the most common causes of postnasal drip is allergies. Seasonal allergies due to plants releasing their pollen may cause trigger postnasal drip, as the body produces extra mucus to try and eliminate the pollen spores.
What is the longest you can live with pulmonary fibrosis?
A diagnosis of PF can be very scary. When you do your research, you may see average survival is between three to five years. This number is an average. There are patients who live less than three years after diagnosis, and others who live much longer.
How fast can pulmonary fibrosis progress?
The rate at which PF progresses can differ significantly from one person to the next. Some people may experience mild to moderate symptoms that worsen slowly over the course of several years; whereas, others may experience “acute exacerbation” in which their symptoms worsen quickly over the course of days or weeks.
Cough 101: An Overview of Cough in Pulmonary Fibrosis
Images related to the topicCough 101: An Overview of Cough in Pulmonary Fibrosis
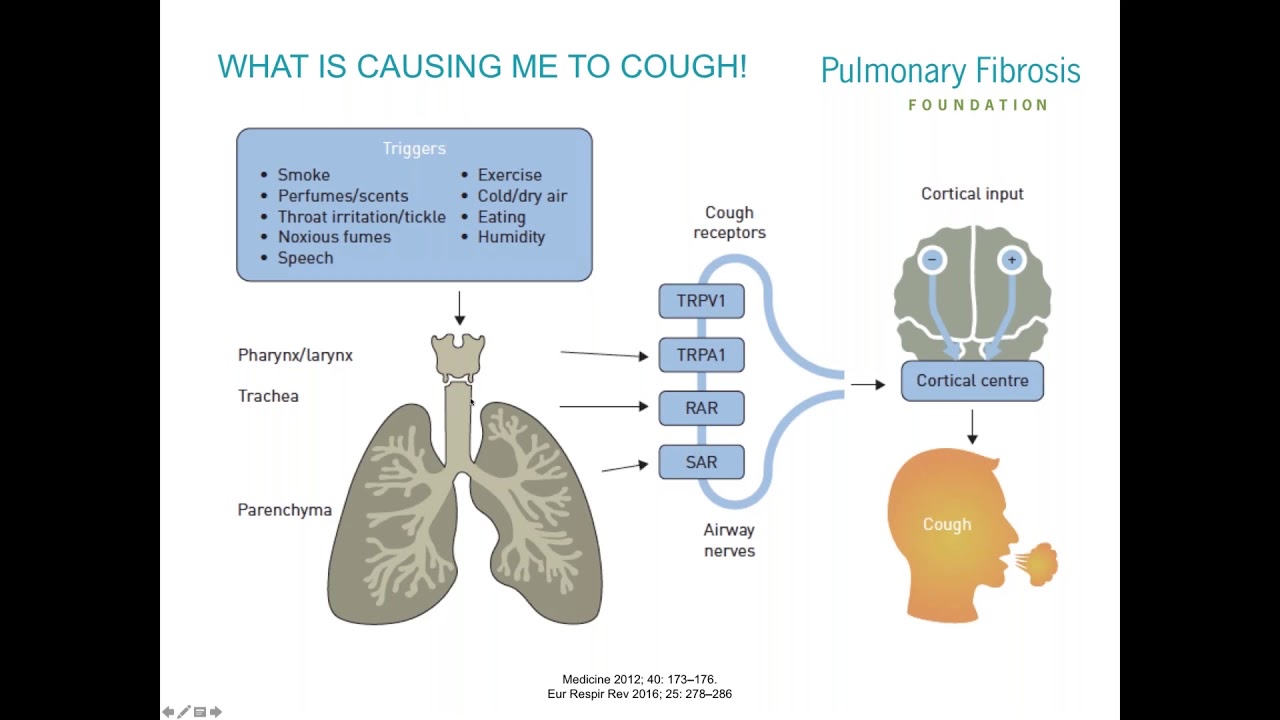
How do you slow the progression of pulmonary fibrosis?
There are 2 medicines that can help slow down the progression of IPF in some people: pirfenidone and nintedanib. Some people also take a medicine called N-acetylcysteine, although its benefits are uncertain.
How do I know if I have fibrosis?
The main symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis are:
breathlessness. a cough that doesn’t go away. feeling tired all the time. clubbing.
Does Covid cause pulmonary fibrosis?
Multiple studies now indicate that increased risk of pulmonary fibrosis followed a severe COVID-19 infection and is mainly observed in patients with comorbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, or coronary disease [8].
What is lung fibrosis Covid?
The persistent respiratory complications may cause substantial population morbidity, long-term disability, and even death due to the lung fibrosis progression. The incidence of COVID-induced pulmonary fibrosis caused by COVID can be estimated based on a 15-year observational study of lung pathology after SARS.
What is the fastest way to get mucus out of your lungs?
Use your stomach muscles to forcefully expel the air. Avoid a hacking cough or merely clearing the throat. A deep cough is less tiring and more effective in clearing mucus out of the lungs. Huff Coughing: Huff coughing, or huffing, is an alternative to deep coughing if you have trouble clearing your mucus.
What naturally kills mucus?
Drinking enough liquids, especially warm ones can help with mucus flow. Water and other liquids can loosen your congestion by helping your mucus move. Try sipping liquids, like juice, clear broths, and soup. Other good liquid choices include decaffeinated tea, warm fruit juice, and lemon water.
What does COPD phlegm look like?
Usually the mucus that people cough up is clear. However, it’s often a yellow color in people with COPD.
What medicine removes mucus from lungs?
Several OTC medications can help clear excess mucus from your lungs. Robitussin and Mucinex, both of which contain guaifenesin, are commonly used expectorants. Expectorants thin and loosen the mucus so that it can be easily coughed up. They can also block the production of mucins, the main protein found in mucus.
How do you get rid of thick mucus in your lungs?
- Keeping the air moist. …
- Drinking plenty of fluids. …
- Applying a warm, wet washcloth to the face. …
- Keeping the head elevated. …
- Not suppressing a cough. …
- Discreetly getting rid of phlegm. …
- Using a saline nasal spray or rinse. …
- Gargling with salt water.
Is it normal to have phlegm everyday?
Your body naturally makes mucus every day, and its presence isn’t necessarily a sign of anything unhealthy. Mucus, also known as phlegm when it’s produced by your respiratory system, lines the tissues of your body (such as your nose, mouth, throat, and lungs), and it helps protect you from infection.
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis – pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, investigation and treatment
Images related to the topicIdiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis – pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, investigation and treatment

Is it normal to have mucus in throat for months?
Catarrh is a build-up of mucus in an airway or cavity of the body. It usually affects the back of the nose, the throat or the sinuses (air-filled cavities in the bones of the face). It’s often temporary, but some people experience it for months or years. This is known as chronic catarrh.
How do I get rid of Covid phlegm?
- stay hydrated.
- inhale steam.
- try lying on either side as flat as you can to help drain the phlegm.
- try moving around to help to move the phlegm.
- try breathing control techniques if you move to an area with a different temperature.
Related searches to Does pulmonary fibrosis cause mucus?
- how does pulmonary fibrosis affect the body
- does pulmonary fibrosis make you cough
- does pulmonary fibrosis cause pneumonia
- miracle cure for pulmonary fibrosis
- living 20 years with pulmonary fibrosis
- does ipf cause mucus
- why does cystic fibrosis cause mucus
- what causes cough in pulmonary fibrosis
- does pulmonary fibrosis come on suddenly
- best cough medicine for pulmonary fibrosis
- does pulmonary fibrosis cause mucus
- what does pulmonary fibrosis cough sound like
- does cystic fibrosis cause pulmonary fibrosis
- pulmonary fibrosis mucus in throat
- does pulmonary fibrosis cause fluid in lungs
- pulmonary fibrosis coughing fits
- pulmonary fibrosis coughing at night
- pulmonary fibrosis stage 4 symptoms
- how to stop coughing from pulmonary fibrosis
Information related to the topic Does pulmonary fibrosis cause mucus?
Here are the search results of the thread Does pulmonary fibrosis cause mucus? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Does pulmonary fibrosis cause mucus?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.
