Table of Contents
What is the truth about OS1 and OS2 optical fiber?
The truth is, OS1 and OS2 fiber are just different names for the same type of fiber:single-mode fiber. They both use the same type of core and cladding and can transmit light over the same distance. The only difference is the size of the fiber’s cladding.
OS1 fiber has a cladding diameter of 125 micrometers, while OS2 fiber has a cladding diameter of 90 micrometers.
* This difference in cladding size is mainly for mechanical strength and compatibility with connectors. The smaller cladding of OS2 fiber makes it more robust and better suited for high-density cabling applications.
However, both OS1 and OS2 fiber have the same optical characteristics, meaning they both have the same low attenuation and dispersion, which makes them suitable for long-distance transmission.
It’s important to note that both OS1 and OS2 fiber can also be used in multimode applications, but this is less common. Multimode fiber is typically used for shorter distances and is often referred to as OM1, OM2, OM3, or OM4.
So, when choosing between OS1 and OS2 fiber, it’s really about your specific application and requirements. If you need a fiber that’s more robust and compatible with smaller connectors, then OS2 is the better choice. But if you’re just looking for a standard single-mode fiber, OS1 is perfectly fine.
Is g652d OS1 or OS2?
The difference between OS1 and OS2 optical fibers lies in their water peak characteristics. OS1 covers all singlemode fibers that meet the ITU-T G.652 standards. These standards don’t specifically address water peak. On the other hand, OS2 fibers are specifically designed to have a low water peak.
Why is this important?
Water peak refers to a specific wavelength of light that can be absorbed by water molecules. In optical fibers, this absorption can lead to signal loss.
OS2 fibers minimize this water peak absorption, resulting in lower signal loss and improved performance.
This is particularly important for longer distances and higher data rates, as the signal needs to travel further with less attenuation. G652D fibers are designed for these applications, which is why they fall under the OS2 category.
Is OS1 obsolete?
Let’s delve a little deeper into why OS2 has become the preferred choice. The key difference lies in the fiber’s core diameter. OS2 fibers have a larger core diameter compared to OS1 fibers. This larger core diameter allows for the transmission of light signals with less distortion and attenuation. This results in faster data rates and the ability to transmit signals over longer distances without significant signal degradation. Additionally, the loose-tube design of OS2 fibers enhances their flexibility and resilience, making them less prone to damage during installation and handling.
In summary, OS2 fibers offer significant advantages over OS1 fibers in terms of performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. While OS1 might still be found in older network infrastructure, it’s unlikely to be implemented in new projects. OS2 has become the standard for modern high-speed optical networks and is expected to remain so for the foreseeable future.
Can OS1 support 100G?
But why is that? Let’s break it down. Fiber optic cables are categorized by their mode – single-mode (SM) or multi-mode (MM). The difference lies in the core size and the way light travels through it. OS1 is a multi-mode fiber optic cable. Think of multi-mode cables as having a larger core size, allowing light to travel in various paths or “modes.” This makes multi-mode cables more susceptible to modal dispersion, where light pulses spread out and become distorted. This can lead to signal degradation and limitations on the speed at which data can be transmitted.
Single-mode fiber cables, on the other hand, have a much smaller core size. This means the light travels in a single path and reduces modal dispersion. That’s why single-mode cables like OS2 and OS3 can handle faster speeds like 40G and 100G.
So, if you’re looking for speeds beyond 10G, you’ll need to consider single-mode fiber cables.
Can OS1 connect to OS2?
OS1 fiber has a core diameter of 9 microns, while OS2 has a core diameter of 8.3 microns. This difference might seem small, but it significantly affects the signal quality. Connecting an OS2 cable to an OS1 cable will cause light to leak out of the smaller core, resulting in a weaker signal and potential performance issues.
Let me explain further. OS1 cables were designed for longer distances and lower data speeds, while OS2 cables are designed for shorter distances and higher data speeds. OS2 cables offer better performance due to their smaller core size, which allows for tighter light confinement and reduced signal loss.
To avoid signal issues, it’s crucial to use the correct fiber cable type for your application. If you need to connect devices using different fiber types, you’ll need to use a fiber optic media converter or a multimode to single-mode adapter to ensure compatibility.
Is OS2 single mode or multimode?
Let’s delve a bit deeper into the specifics of OS2. OS2 is commonly used with wavelengths of 1310 nm and 1550 nm. These wavelengths are ideal for long-distance data transmission and are particularly beneficial for applications like fiber optic internet.
The 9/125 µm size of the fiber refers to the core diameter and cladding diameter, respectively. This small core size is essential for ensuring single-mode transmission. The smaller core allows for tighter control of the light path, reducing signal dispersion and interference.
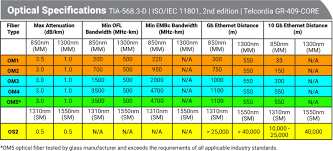
Now, let’s talk about the attenuation of OS2. It has a maximum attenuation of 0.4 dB/km. Attenuation refers to the loss of signal strength as it travels through the fiber. The lower the attenuation, the further the signal can travel before needing amplification. OS2’s low attenuation makes it ideal for long-distance communications.
Remember, OS2 is a single-mode fiber, optimized for high-speed data transmission over long distances. Its small core size, specific wavelengths, and low attenuation make it a reliable choice for various fiber optic applications.
See more here: Is G652D Os1 Or Os2? | Are Os1 And Os2 Compatible
What is the difference between OS1 and OS2 cables?
OS2 cables are designed for longer distances compared to OS1 cables, allowing for transmissions up to 10 kilometers. The Ethernet transmission speed for both types of cables falls between 1 and 10 gigabits per second. So, which cable is right for your needs? It’s all about the specifics. Factors to consider include:
Application: What’s the intended use of the cable? Are you setting up a high-speed network in a large building or a smaller office?
Location: Will the cable be installed indoors or outdoors? Outdoor installations may require a more robust cable.
Cable-laying Method: How will the cable be installed? Will it be run through conduits, buried underground, or suspended overhead?
Transmission Distance: What’s the maximum distance that needs to be covered?
Budget: OS2 cables are generally more expensive than OS1 cables due to their increased capabilities.
Choosing the right cable is essential for achieving reliable and efficient network performance. Taking these factors into account can help you make the right choice for your specific needs.
Going Deeper
Let’s break down some of the factors in more detail:
Application:
OS1 is ideal for short-distance applications like connecting workstations to a network switch or within a server room.
OS2 excels in scenarios requiring longer runs, like connecting buildings or campuses.
Location:
OS1 can be suitable for indoor installations, particularly in controlled environments.
OS2 is better suited for outdoor installations as its thicker cladding provides greater protection against harsh weather and environmental factors.
Cable-laying Method:
OS1 can be used for various installations, including conduits and trays.
OS2 is often preferred for installations requiring greater flexibility or resistance to damage, like direct burial or overhead runs.
Transmission Distance:
OS1 is generally limited to shorter distances, typically under 3 kilometers.
OS2 can handle longer distances of up to 10 kilometers, making it suitable for larger networks with distributed infrastructure.
Budget:
OS1 is typically more cost-effective than OS2.
OS2 offers greater performance and longevity but comes at a higher price.
Choosing between OS1 and OS2 cables ultimately boils down to a balance of these factors. By carefully assessing your needs, you can make an informed decision that optimizes performance and cost.
Does OS1 work With OS2?
OS1 fiber is an older type of single-mode fiber cable that can operate at both 1310nm and 1550nm wavelengths. OS2 fiber is the newer, more common standard for single-mode fiber cables. OS2 fiber also operates at these wavelengths but meets the ITU-T G.652D and G.657A1 specifications, which are designed for improved performance and reliability.
So, while OS1 is an older technology, it can still be used with OS2 fiber as long as the connections are compatible. The reason for this compatibility is that both OS1 and OS2 fibers are designed to transmit light at the same wavelengths, meaning the light signals can be transmitted through either type of fiber.
Let’s dive a bit deeper into what this compatibility means for you:
Flexibility: You can mix and match OS1 and OS2 fiber in your network without worrying about them not working together.
Upgrading: If you have existing OS1 infrastructure, you can upgrade to OS2 for better performance without completely replacing everything.
Cost-effective: Sometimes, it might be more cost-effective to use OS1 fiber in certain parts of your network, especially if you have existing infrastructure.
However, it’s important to keep in mind that OS1 fiber is considered a legacy technology. While it’s compatible with OS2, you might face some limitations:
Lower Bandwidth:OS1 fiber typically has a lower bandwidth capacity compared to OS2.
Limited Availability:OS1 fiber is becoming less readily available as OS2 becomes the industry standard.
Future-proofing: As technology advances, you might find that OS1 fiber cannot support the latest network technologies or applications.
To make sure your network runs smoothly, it’s a good idea to consult with a networking expert to assess your specific needs and determine the best fiber type for your network.
What is the difference between OS1 and OS2 optical fibers?
Think of it this way: OS1 is like a general category, while OS2 is a more specific type. The low water peak characteristic of OS2 fibers is important for certain applications, especially CWDM, which stands for Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing. CWDM is a technology that allows you to transmit multiple signals over a single fiber at different wavelengths.
But why do OS2 fibers excel at CWDM? It’s all about minimizing signal loss. The presence of water molecules inside the fiber can cause light to scatter, which weakens the signal. By reducing the water peak, OS2 fibers help maintain a stronger signal over longer distances.
Here’s a simple table to summarize the key differences:
| Feature | OS1 | OS2 |
|—————-|—————–|—————-|
| Water Peak | Standard | Low |
| CWDM Suitable | No | Yes |
| ITU-T Standard | G.652 | G.652C, G.652D |
So, when choosing between OS1 and OS2 fibers, consider your specific needs. For standard single-mode applications, OS1 fibers are a good choice. But if you’re working with CWDM or need to minimize signal loss, OS2 fibers are the better option.
Can OS1 and OS2 fiber be mixed?
Here’s the thing: OS2 fiber is a newer, more advanced type of fiber optic cable. It carries more data than OS1, and the signal travels farther without losing strength. That’s why it’s the go-to choice for high-speed networks.
But don’t worry if you have OS1 already – you don’t have to rip everything out and start over. You can use OS1 and OS2 together, but you need to make sure your network gear can handle both types.
Here’s what to keep in mind:
Transceivers: These are the devices that convert the light signals in fiber optic cable into electronic signals that your network equipment can understand. Make sure your transceivers are compatible with both OS1 and OS2 fibers.
Patch Panels: These are the panels that hold and organize your fiber optic cables. Ensure that your patch panels support both OS1 and OS2 cables.
To figure out if your network gear is up to snuff, check the specifications. They should tell you what types of fiber optic cables they can handle.
If you’re not sure about any of this, it’s always a good idea to talk to a networking expert. They can help you make sure your network is set up for success, no matter what kind of fiber optic cables you’re using.
See more new information: musicbykatie.com
Are Os1 And Os2 Compatible: A Quick Guide
The simple answer is no, OS/1 and OS/2 aren’t compatible. They’re like two different languages that can’t understand each other.
Think of it this way: OS/1 is a single-tasking operating system. Back in the day, it was the go-to for personal computers. It’s like having one room in your house. You can only do one thing in that room at a time.
OS/2, on the other hand, was designed to be a multitasking operating system. Imagine it as a house with multiple rooms. You can cook in the kitchen, watch TV in the living room, and work in your office, all at the same time. It was IBM’s answer to Microsoft Windows, and it was pretty popular for a while.
So, why are they not compatible? Think of it like trying to fit a square peg into a round hole. They were built with different architectures and use different languages. They’re like apples and oranges – they’re both fruits, but they taste different and have different uses.
Now, there are a few things to remember:
OS/1 was pretty much replaced by MS-DOS. Think of MS-DOS as a newer version of OS/1 with a few extra features.
OS/2 eventually evolved into eComStation, which is still available today. It’s like a modern version of OS/2, but it’s not as widely used as Windows or macOS.
So, if you’re looking to run OS/1 and OS/2 on the same computer, you’re out of luck. They’re not compatible. But, you can always find old computers that run these operating systems.
Is There Any Way to Run Both OS/1 and OS/2 on the Same Computer?
You can’t directly run OS/1 and OS/2 on the same computer. They just weren’t designed to work together. However, you can use a virtual machine (VM) to simulate a different computer environment. Think of it as a virtual “room” within your computer.
You can use software like VirtualBox or VMware to create a virtual machine and install either OS/1 or OS/2 inside of it. This way, you can run both operating systems on the same computer, but they’ll be isolated from each other. It’s like having two separate houses within the same city.
What About Emulators?
Emulators are a bit different from virtual machines. They try to mimic the behavior of a different computer system. Think of it as wearing a costume to pretend you’re someone else.
You can find emulators for OS/1 and OS/2 that let you run older programs designed for those systems on your modern computer. It’s like watching a classic movie from the 1980s on your modern TV.
Is OS/2 Still Relevant Today?
OS/2 is pretty much a relic of the past. It’s like a vintage car – it’s cool to look at, but it’s not practical for daily use. Today, Windows and macOS dominate the operating system market.
However, some people still use OS/2 for nostalgic reasons or because they need to run older programs that are incompatible with newer operating systems. It’s like having a favorite old sweater that you still wear even though it’s out of style.
FAQs
Q: What are some of the key differences between OS/1 and OS/2?
A: OS/1 was a single-tasking operating system, while OS/2 was a multitasking operating system. OS/1 was also designed for simpler computers, while OS/2 was designed for more powerful computers.
Q: Is OS/2 compatible with Windows?
A: No, OS/2 and Windows are not compatible. They’re two different operating systems with different architectures.
Q: Can I use OS/2 to run Windows programs?
A: No, OS/2 cannot run Windows programs. They’re not compatible.
Q: Is OS/2 still being developed?
A: OS/2 is no longer being developed by IBM. However, it’s still being maintained by a community of developers. Think of it like a classic car that’s been restored to its former glory.
Q: Is OS/2 better than Windows?
A: That’s a matter of opinion. OS/2 and Windows have their strengths and weaknesses. OS/2 was known for its stability and multitasking capabilities, while Windows has a wider range of software and games available.
Q: Can I install OS/2 on a modern computer?
A: You can technically install OS/2 on a modern computer, but it’s not recommended. OS/2 was designed for older hardware and might not work properly on modern systems. It’s like trying to fit a vintage phone into a modern phone case.
If you’re interested in trying out OS/2, you can use a virtual machine or an emulator.
Q: What are some of the advantages and disadvantages of using OS/2?
A: OS/2 was known for its stability and multitasking capabilities. It also had a good set of built-in applications. However, it lacked the widespread software support of Windows, and its user interface was considered less user-friendly by some.
OS/1 and OS/2 are fascinating examples of how operating systems have evolved over time. They may be relics of the past, but they played a significant role in shaping the computing landscape we know today.
Comparison Between OS1 and OS2 SMF Cables | FS Community
OS1 vs OS2 SMF Cables, What Are Their Differences? Standard OS1 SMF cables are compliant with the specifications of ITU-T G.652, including ITU-T G.652A and ITU-T G.652B standards (conventional), ITU-T G.652C and G.652D standards (low FS Community
The Ultimate Guide to Choose Between OS1 and OS2 – QSFPTEK
What are the differences between OS1 vs OS2? How to choose between fiber OS1 vs OS2? This post will tell you about every aspect of their standard, structure, qsfptek.com
OS1 and OS2 SMF fiber Cables: A Comprehensive Comparison
OS1 and OS2 cables are both types of single-mode fiber cables, but they have several key differences. OS1 cables are predominantly used for indoor applications ascentoptics.com
The Truth About OS1 and OS2 Optical Fiber
Besides the difference in link distance, OS1 and OS2 fibers have different attenuation—OS2 has two times fewer losses than OS1 fomsn.com
Difference Between OS1 vs OS2 Single Mode Fiber
OS1 and OS2 are cabled single mode optical fiber specifications. In fact, there are many differences between OS1 vs OS2 single mode fiber. This text will make a comparison between OS1 vs Fiber Optic Cabling Solutions
What are the differences between OS1 and OS2 fiber?
OS1 fibers are designed for short-distance applications, typically up to 10 kilometers (6 miles). In contrast, OS2 fibers can support much longer distances, up to 200 kilometers cableandconnections.com
OS1 singlemode fiber vs. OS2 singlemode fiber – Wiki
Singlemode fiber can be further classified as OS1 and OS2 singlemode fiber. This article will compare OS1 with OS2 singlemode fiber, list the pros and cons, and illustrate why we recommend you to replace teleweaver.com
The Difference between OS1 and OS2 Optical Fibre. Why it
OS1 cables display greater attenuation, meaning greater loss of signal strength than OS2 cables. The maximum attenuation of OS1 fibre cable is 1.0db/km Apollo Technology
OS1 and OS2 Single mode optical fiber standards – Questtel
The difference between OS1 and OS2 optical fibers lies in the fact that OS1 covers all the singlemode fibers that complies with ITU-T G.652 characteristics. On the other hand QuestTel
Os1 Vs Os2 Fibre Optic Cable Standards
Single-Mode Fiber Is Usually Divided Into Os1 And Os2 Single-Mode Fiber!
Os2 Single Mode Fiber Patch Cable | Fs
What Is The Difference Between Om3 And Os2 Fiber Optic Cable?
Which Is The Fastest Fiber Optic Cable? Os2 Or Om1?
What Is Os1 – Video 15
🌟How To Install Two Operating Systems On Two Physical Drives, On A Desktop Computer Or Laptop
Dual Boot Prime Os Và Windows 10
Link to this article: are os1 and os2 compatible.
See more articles in the same category here: https://musicbykatie.com/wiki-how/
