Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Does inelastic collision conserve momentum?“? We answer all your questions at the website Musicbykatie.com in category: Digital Marketing Blogs You Need To Bookmark. You will find the answer right below.
An inelastic collision is a collision in which there is a loss of kinetic energy. While momentum of the system is conserved in an inelastic collision, kinetic energy is not.Elastic collisions are those in which both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved. Inelastic collisions are those in which either momentum or kinetic energy is not conserved.An inelastic collisions occurs when two objects collide and do not bounce away from each other. Momentum is conserved, because the total momentum of both objects before and after the collision is the same.
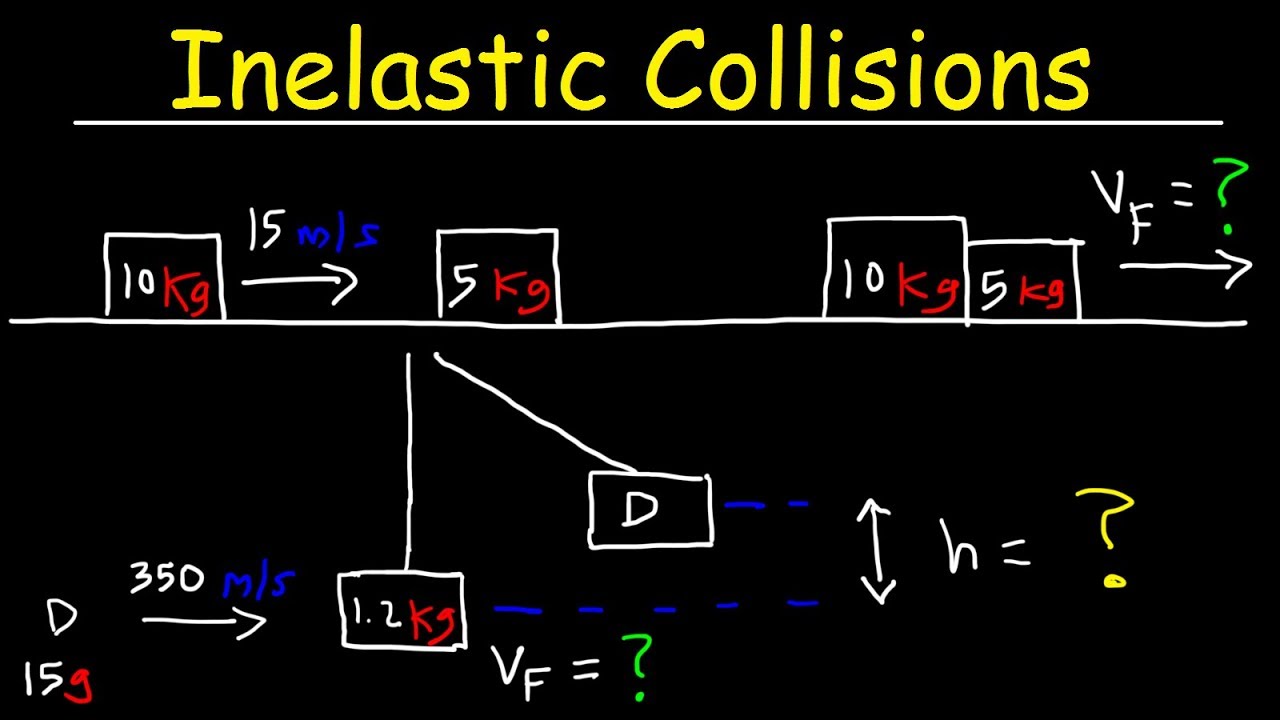
Table of Contents
Is momentum conserved in elastic and inelastic collisions?
Elastic collisions are those in which both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved. Inelastic collisions are those in which either momentum or kinetic energy is not conserved.
Do inelastic collisions conserve total momentum?
An inelastic collisions occurs when two objects collide and do not bounce away from each other. Momentum is conserved, because the total momentum of both objects before and after the collision is the same.
Inelastic Collision Physics Problems In One Dimension – Conservation of Momentum
Images related to the topicInelastic Collision Physics Problems In One Dimension – Conservation of Momentum

Is momentum conserved in an inelastic explosion?
An inelastic collision does not conserve kinetic energy. Momentum is conserved regardless of whether or not kinetic energy is conserved.
Is momentum conserved during a collision?
Momentum is conserved in the collision. Momentum is conserved for any interaction between two objects occurring in an isolated system. This conservation of momentum can be observed by a total system momentum analysis or by a momentum change analysis.
In which type of collision is momentum conserved?
Elastic collisions are collisions in which both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved. The total system kinetic energy before the collision equals the total system kinetic energy after the collision.
Why do inelastic collisions not conserve energy?
An inelastic collision is one in which the internal kinetic energy changes (it is not conserved). This lack of conservation means that the forces between colliding objects may remove or add internal kinetic energy. Work done by internal forces may change the forms of energy within a system.
Why is momentum lost in a collision?
Provided that there are no net external forces acting upon the objects, the momentum of all objects before the collision equals the momentum of all objects after the collision. If there are only two objects involved in the collision, then the momentum lost by one object equals the momentum gained by the other object.
See some more details on the topic Does inelastic collision conserve momentum? here:
Why is momentum conserved in an inelastic collision and …
The conservation of momentum is simply a statement of Newton’s third law of motion. During a collision the forces on the colliding bodies …
Inelastic Collision – The Physics Classroom
Elastic collisions are collisions in which both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved. The total system kinetic energy before the collision equals the total …
Inelastic Collisions in One Dimension – College Physics
An inelastic one-dimensional two-object collision. Momentum is conserved, but internal kinetic energy is not conserved. (a) Two objects of equal mass …
Elastic and Inelastic Collisions – Hyperphysics
Momentum is conserved in inelastic collisions, but one cannot track the kinetic energy through the collision since some of it is converted to other forms of …
What is conserved in an inelastic collision?
An inelastic collision is a collision in which there is a loss of kinetic energy. While momentum of the system is conserved in an inelastic collision, kinetic energy is not.
What happens to colliding objects during an inelastic collision?
An inelastic collision is one in which objects stick together after impact, and kinetic energy is not conserved. This lack of conservation means that the forces between colliding objects may convert kinetic energy to other forms of energy, such as potential energy or thermal energy.
Elastic and Inelastic Collisions
Images related to the topicElastic and Inelastic Collisions

What is the difference between elastic collision and inelastic collision?
A perfectly elastic collision is defined as one in which there is no loss of kinetic energy in the collision. An inelastic collision is one in which part of the kinetic energy is changed to some other form of energy in the collision.
Why is momentum conserved in all types of collisions?
Impulses of the colliding bodies are nothing but changes in momentum of colliding bodies. Hence changes in momentum are always equal and opposite for colliding bodies. If the momentum of one body increases then the momentum of the other must decrease by the same magnitude. Therefore the momentum is always conserved.
Is velocity conserved in an inelastic collision?
Perfectly Inelastic Collision
Momentum is conserved, but internal kinetic energy is not conserved. (a) Two objects of equal mass initially head directly toward one another at the same speed. (b) The objects stick together (a perfectly inelastic collision), and so their final velocity is zero.
What is always conserved in all types of collision?
Momentum is conserved in all types of collision whether it is elastic or inelastic where as kinetic energy is lost in sound energy in the absence of external force in inelastic collision.
How do you find momentum after inelastic collision?
If inelastic, then the total amount of system momentum before the collision (and after) can be determined by using the Pythagorean theorem. Since the two colliding objects travel together in the same direction after the collision, the total momentum is simply the total mass of the objects multiplied by their velocity.
Is momentum always conserved?
In collisions between two isolated objects Newton’s third law implies that momentum is always conserved. In collisions, it is assumed that the colliding objects interact for such a short time, that the impulse due to external forces is negligible.
When both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved?
Elastic collisions are collisions in which both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved. The total system kinetic energy before the collision equals the total system kinetic energy after the collision. If total kinetic energy is not conserved, then the collision is referred to as an inelastic collision.
Momentum (6 of 16) Inelastic Collisions, An Explanation
Images related to the topicMomentum (6 of 16) Inelastic Collisions, An Explanation

When we say that momentum is conserved we mean?
For any collision occurring in an isolated system, momentum is conserved. The total amount of momentum of the collection of objects in the system is the same before the collision as after the collision.
How does momentum before an inelastic collision compare to the momentum after the collision?
Since the total system momentum before the collision is the same as it is after the collision, the total momentum of the system can be considered to be conserved.
Related searches to Does inelastic collision conserve momentum?
- does elastic collision conserve momentum
- what is conserved in an elastic collision
- in which is momentum conserved in elastic collision or an inelastic collision
- do perfectly inelastic collisions conserve momentum
- how is momentum conserved in inelastic collisions
- why do inelastic collisions conserve momentum
- why is momentum conserved
- elastic and inelastic collisions examples
- is momentum conserved inelastic collision
- does conservation of momentum apply to inelastic collisions
- is energy conserved in an inelastic collision
- difference between elastic and inelastic collision
- does inelastic collision conserve momentum
- what is conserved in an inelastic collision
- what is a perfectly inelastic collision
Information related to the topic Does inelastic collision conserve momentum?
Here are the search results of the thread Does inelastic collision conserve momentum? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Does inelastic collision conserve momentum?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.
